Table 4. Edges present in the best-fitting models in human (BIC scores).
| Number of edges | Number of unique best-fitting models (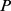 ) ) |
Basic set of edges | Additional edges |
| 1 | 4 | (A,B) | |
| 2 | 5 | (A,B), (B,D) | |
| 3 | 13 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C) | |
| 4 | 20 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E) | (E,C), (A,E), (A,D) |
| 5 | 22 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E), (E,C) | (A,D) |
| 6 | 25 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E), (E,C), (A,D) | |
| 7 | 20 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E), (E,C), (A,D), (A,E) | |
| 8 | 26 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E), (E,C), (A,D), (A,E), (B,C) | |
| 9 | 15 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E), (E,C), (A,D), (A,E), (B,C), (C,D) | |
| 10 | 1 | (A,B), (B,D), (A,C), (B,E), (E,C), (A,D), (A,E), (B,C), (C,D), (E,D) |
For each fixed number of edges
 , we report the basic set of edges (the most supported
, we report the basic set of edges (the most supported  edges), as well as additional edges that are not significantly less supported (at Bonferroni-corrected significance level 0.05).
edges), as well as additional edges that are not significantly less supported (at Bonferroni-corrected significance level 0.05).
