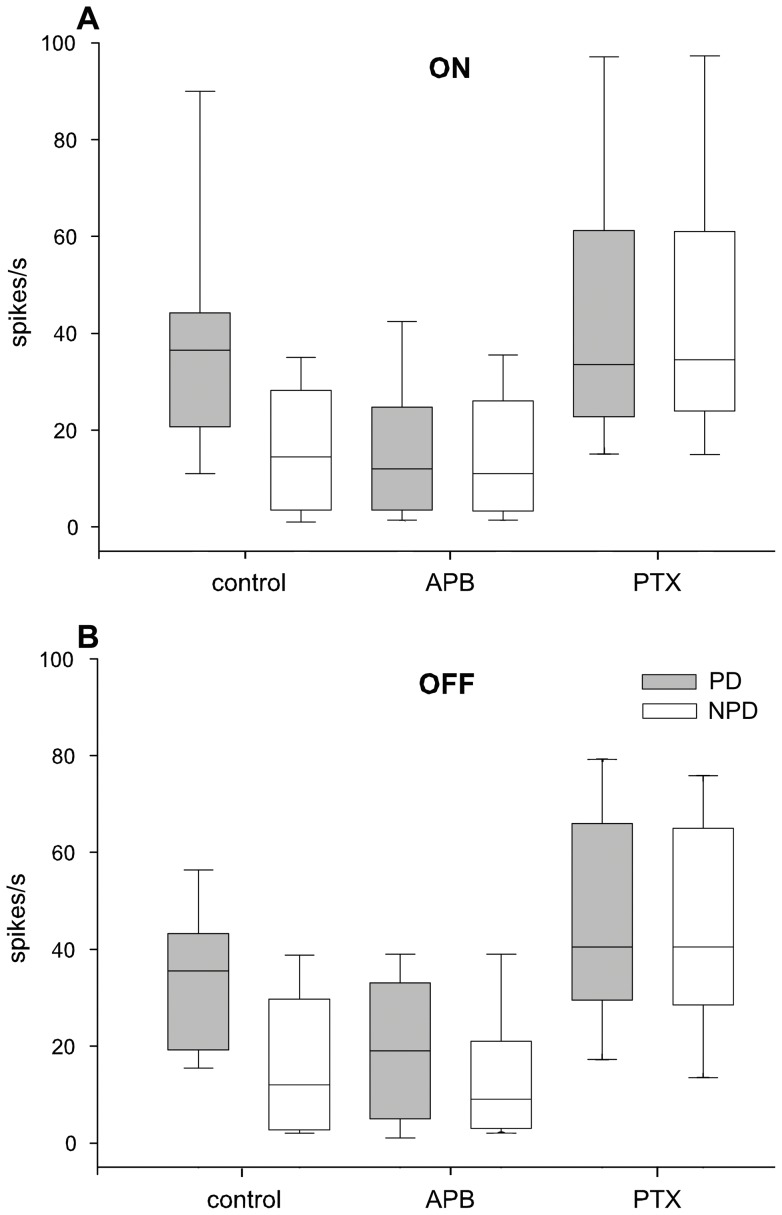
Figure 5. Effects of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrat (APB) and picrotoxin (PTX) on neuronal activity in all units tested.
Neuronal responses in all 25 single- and multi-unit recordings during ON A) and OFF (B) stimulation in preferred (PD, grey boxes) and non-preferred (NPD, white boxes) direction before (control; left 2 boxes), after intravitreous application of the drug APB (middle 2 boxes) and after subsequent intravitreous application of PTX (right 2 boxes). Horizontal lines indicate the median, boxes the 25–75%, and whiskers the 10–90% percentiles of non-parametric statistical comparison. Ordinate: neuronal activity in spikes per second, abscissa: experimental conditions. At approximately 100–200 µM intravitreal concentration, APB completely blocks the response driven by the moving ON stimulus (p<0.005) but also decreases the response to the moving OFF stimulus (p<0.05). The activity in the non-preferred direction is unaltered as is spontaneous activity. PTX increases the responses in PD and in NPD to about the same values during ON- as well as during OFF stimulation.