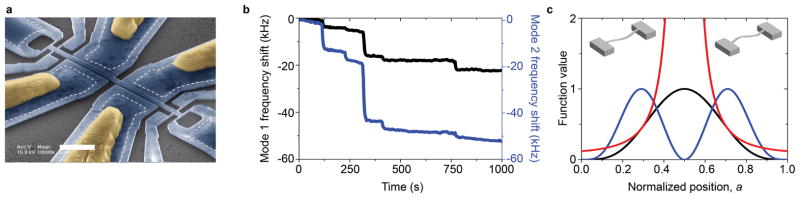
Figure 1. Multimode NEMS-based mass detection in real time.
a, Colorized electron micrograph of a representative device used in this study. The white dotted line shows the boundaries of the region beneath the suspended device that anchors it to the substrate. Yellow regions represent Al/Si gate contacts. Positioned near the ends of the beam are narrow gauges that become strained with motion of the beam and thereby enable transduction of mechanical motion into electric resistance. The white scale bar is 2 microns. b, Time-correlated resonant frequency shifts of the two modes (mode 1 (black) and mode 2 (blue)) corresponding to individual gold nanoparticles landing on the NEMS. The frequency offsets are 44.6 MHz and 105.0 MHz for the first and second modes respectively. c, Responsivities of the first two modes of a doubly-clamped beam (black=mode 1, blue = mode 2) and their ratio, G (red). Insets: Mode shapes for the first and second in-plane modes.