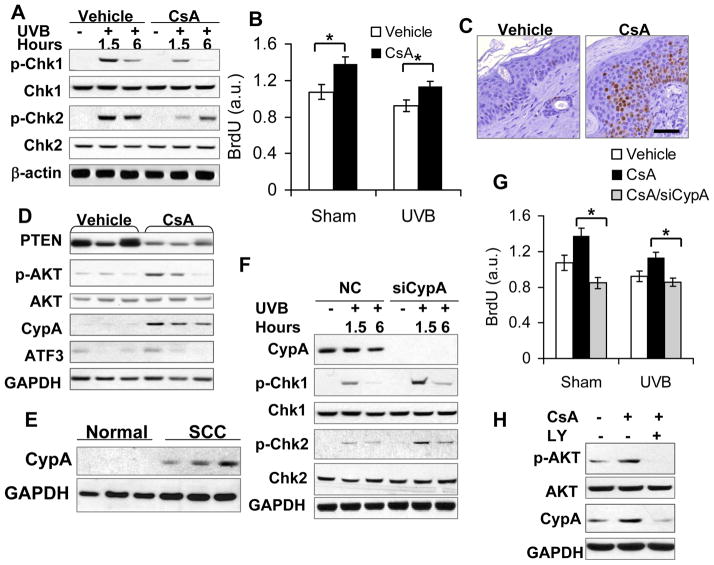
Fig. 5.
CsA disrupts UVB-induced checkpoint activation through AKT-dependent CypA up-regulation. A, immunoblot analysis of p-Chk1 (serine 345), Chk1, p-Chk2 (Threonine 68), Chk2, and β-actin in vehicle- and CsA-treated HaCaT cells at 1.5 and 6 h post-UVB (20 mJ/cm2). B, BrdU incorporation ELISA assay of vehicle- and CsA-treated HaCaT cells post-sham or -UVB irradiation. *, P < 0.05, significant difference between vehicle and CsA treatment. C, immunohistochemical analysis of Ki67-positive cells in vehicle and CsA-treated non-tumor mouse skin irradiated with UVB three times a week for 25 weeks. Scale Bar: 50 μm. D, immunoblot analysis of PTEN, p-AKT, AKT, CypA, ATF3 and GAPDH in vehicle and CsA-treated mouse skin as in C. E, immunoblot analysis of CypA protein levels in normal human skin and SCC specimens. F, immunoblot analysis of CypA, p-Chk1, Chk1, p-Chk2, Chk2, GAPDH in CsA-treated HaCaT cells transfected with negative control (NC) siRNA or siRNA targeting CypA (siCypA) at 1.5 or 6 h post-UVB (20 mJ/cm2). G, BrdU incorporation ELISA assay of vehicle-treated, CsA-treated, CsA-treated/siCypA-transfected HaCaT cells post-sham or -UVB irradiation. *, P < 0.05, significant difference in CsA-treated HaCaT cells between NC and siCypA treatment. H, immunoblot analysis of p-AKT, AKT, CypA and GAPDH in vehicle-treated, CsA-treated, and CsA/LY-treated HaCaT cells.