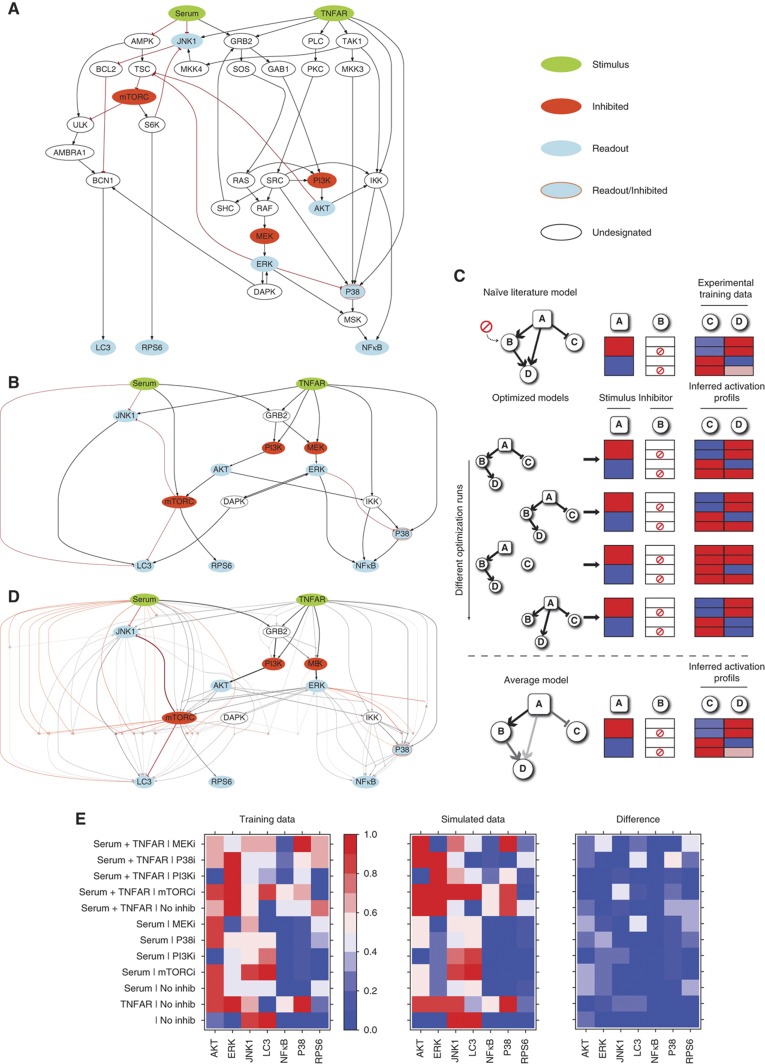
Figure 4.
Assembly and optimization of a literature-derived growth model. (A) An extensive literature and database search has been carried out to assemble a literature-derived signed directed graph modeling the cross-talk between growth pathways. The network is visualized by the graph layout routine included in the CellNOpt software. (B) The graph in (A) was automatically compressed by the CellNOpt software by applying the rules described by Saez-Rodriguez et al (2009). White ovals circled with dashed lines in (A), represents nodes, not subjected to experimental manipulation, that were part of linear cascades in which a series of undesignated nodes and edges impinged on a designated node. Such nodes were compressed by CellNOpt and consequently eliminated, as shown in (B). (C) Schematic representation of the optimization strategy of a toy network. The CellNOpt software uses a genetic algorithm to identify models whose prediction better explains the experimental results. Edges are randomly removed and connected by different combinations of AND/OR logic gates. The resulting rewired models are finally tested for their ability to reproduce the experimental results. Since different optimization runs yield models with different connections, the performance of the model is obtained by averaging the predictions of 1000 different models. (D) A graph representing the average results of 1000 optimization runs. The thickness and color intensity of each edge are proportional to the number of times it appears in the 1000 optimized models. (E) Color coded representation of the results of the experiments that were used to train the model and comparison with the average prediction of the 1000 models. The protein activation level, which ranges from 0 to 1, is represented with a gradient from blue (inactive) to red (active). The third panel uses the same color scale to display the absolute value of the difference between the data simulated from the model and the experimental data used for training.