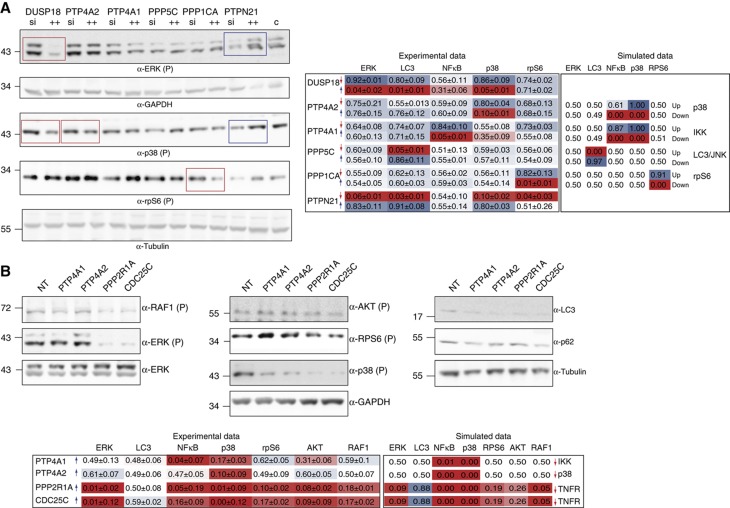
Figure 6.
Validation of phosphatase hits mapping prediction on the optimized growth model. (A) Comparison of phenotypes obtained after downregulation and upregulation of selected phosphatase genes. The results of the screening are represented with a color code where red and blue indicate that the phosphatase downregulates or upregulates the activation of the readout indicated on the right of the panel. Phosphatases were overexpressed (blue arrow) or silenced (red arrow) by an equimolar pool of vectors. After 48 h of transfection, cells were stimulated with TNFα for 10 min. Activation levels of the sentinel proteins were measured by immunoblotting with anti-phospho ERK, anti-GAPDH, anti-phospho p38, anti-phospho rpS6 and anti-tubulin. The nuclear translocation of NFκB was measured by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy coupled to automated image analysis in cells stained with anti-NFκB antibody. The obtained results were normalized by the Hill function to values ranging from 0 to 1 and then compared with the ones obtained by the simulation of the downregulation (red arrow) or upregulation (blue arrow) of specific nodes in the optimized model. Blue and red boxes, respectively, indicate high and low values, while intermediate values are mapped to shades of red and blue. For each measurement, the average value and standard deviation of three independent biological replicas was calculated. (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated phosphatases or with an empty vector. After 24 h of transfection, cells were stimulated with TNFα for 10 min. Anti-V5 and anti-tubulin antibodies were used to assess transfection efficiency and as loading control, respectively. The activation level of the five sentinel proteins was analyzed either by western blot or by immunofluorescence techniques. The phosphorylation levels of RAF1, ERK, AKT, rpS6 and p38 were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-specific antibodies and anti-tubulin. The autophagy level was assessed by revealing protein extracts with anti-LC3 antibody and anti-tubulin, as loading control. As previously described, the nuclear translocation of NFκB was measured by immunofluorescence microscopy coupled to automated image analysis. For each measurement, the average value and standard deviation of four independent biological replicas was calculated. As previously described, the obtained results were normalized by the Hill function to values ranging from 0 to 1 and reported. Source data is available for this figure in the Supplementary Information.