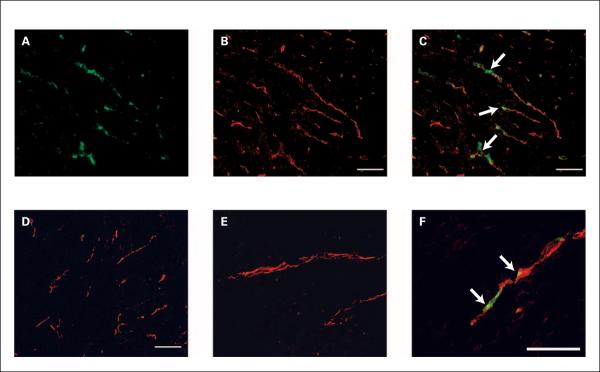
Fig. 6.
Localization of bavituximab to tumor vessels after injection into rats bearing syngeneic Dunning R3227-AT1 prostate tumors. Rats were injected i.v. with bavituximab or rituximab. After 24 h, the rats were exsanguinated and their tumors were removed. A–C show blood vessels in a frozen section of tumor at low magnification. A, stained with biotinylated goat anti-human IgG followed by Cy2-streptavidin (green) to detect localized bavituximab; B, stained with mouse anti-rat CD31 followed by Cy3-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (red) to detect vascular endothelium; C, a merged image of bavituximab localized on CD31-positive endothelium (thick). D, a merged image of blood vessels in the tumor of a rat injected with rituximab. No binding of rituximab was detected. E–F, higher magnification merged images of blood vessels in tumors from rats injected with rituximab (E) or bavituximab (F). Bars, 100 μm.