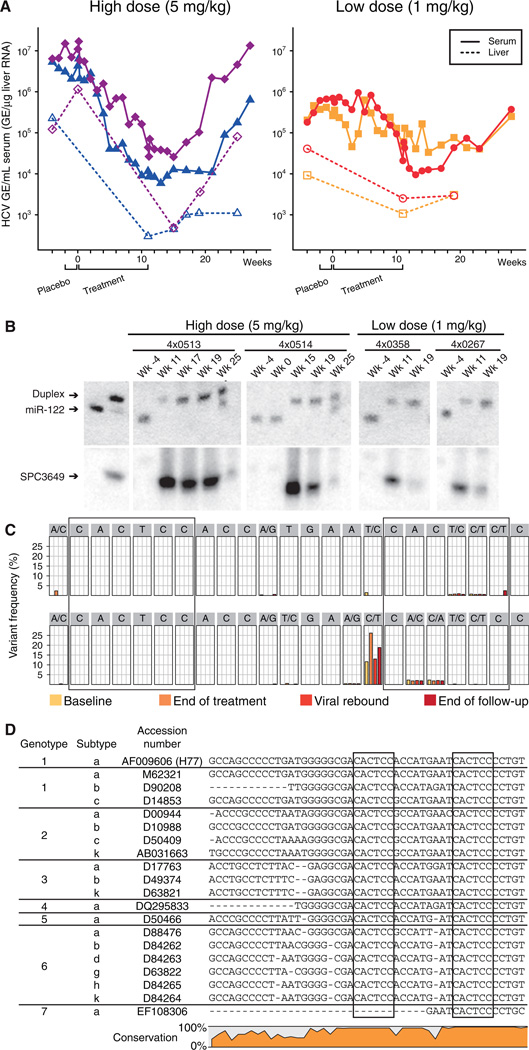
Fig. 1. Silencing of miR-122 by SPC3649 in chimpanzees with chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
(A) Analysis of HCV RNA levels in HCV-infected chimpanzees during the study. The HCV titers are shown as genomic equivalents (GE) for the high-dose animals (4×0513 blue triangles, 4×0514 magenta diamonds) and low-dose animals (4×0267 orange squares, 4×0358 red dots) in serum (GE/mL, solid lines) and liver (GE/µg liver RNA, dashed lines). The placebo and active treatment periods are indicated below. (B) Northern blot analysis of RNA from chimpanzee liver biopsies using LNA-modified probes detecting free and sequestered miR-122 (upper panel) and SPC3649 (lower panel). The first two lanes are positive controls for free miR-122 and preformed miR-122:SPC3649 heteroduplexes, respectively. (C) Detection of sequence variants in the miR-122 seed sites (boxed) by deep sequencing of the HCV 5’ NCR from the high dose animals at four time points: baseline, end of treatment, viral rebound and end of the follow-up period. (D) The two miR-122 seed sites (boxed) in the HCV 5’ NCR are conserved in all HCV genotypes and subtypes (see SOM for details).