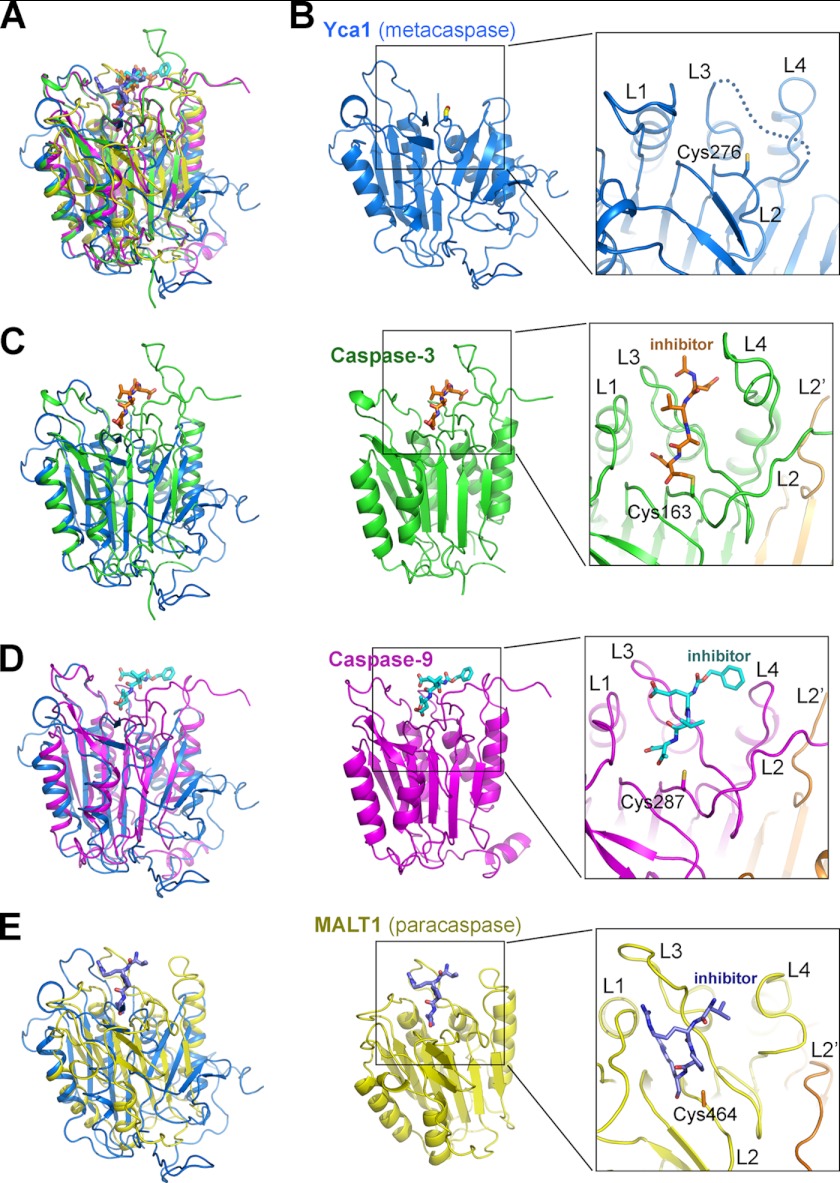
FIGURE 2.
Structural comparison of Yca1 with caspases and the paracaspase MALT1. A, structural overlay of Yca1 (blue), caspase-3 (green), caspase-9 (magenta), and MALT1 (yellow). B, a close-up view of the active site of Yca1. Among the four active site loops, L1, L2, and L4 exhibit well defined conformation. A large portion of the L3 loop (dotted line), however, is disordered, likely due to its flexible nature in the absence of substrate binding. C, comparison of Yca1 (PDB code 4F6O) with caspase-3 (PDB code 1CP3 (28)). A close-up view on the caspase-3 active site is shown. The covalently bound inhibitor acetyl-Asp-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone (Ac-DVAD-fmk) is highlighted in orange. D, comparison of Yca1 with caspase-9 (PDB code 1JXQ (29)). A close-up view on the caspase-9 active site is shown. The covalently bound inhibitor benzyloxycarbonyl-Glu-Val-Asp-dichlorobenzylmethyl ketone (z-EVD-dcbmk) is highlighted in cyan. E, comparison of Yca1 with the paracaspase MALT1 (PDB code 3UOA (30)). A close-up view on the MALT1 active site is shown. The covalently bound inhibitor benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Arg-Pro-Arg (z-VRPR-fmk) is highlighted in purple.