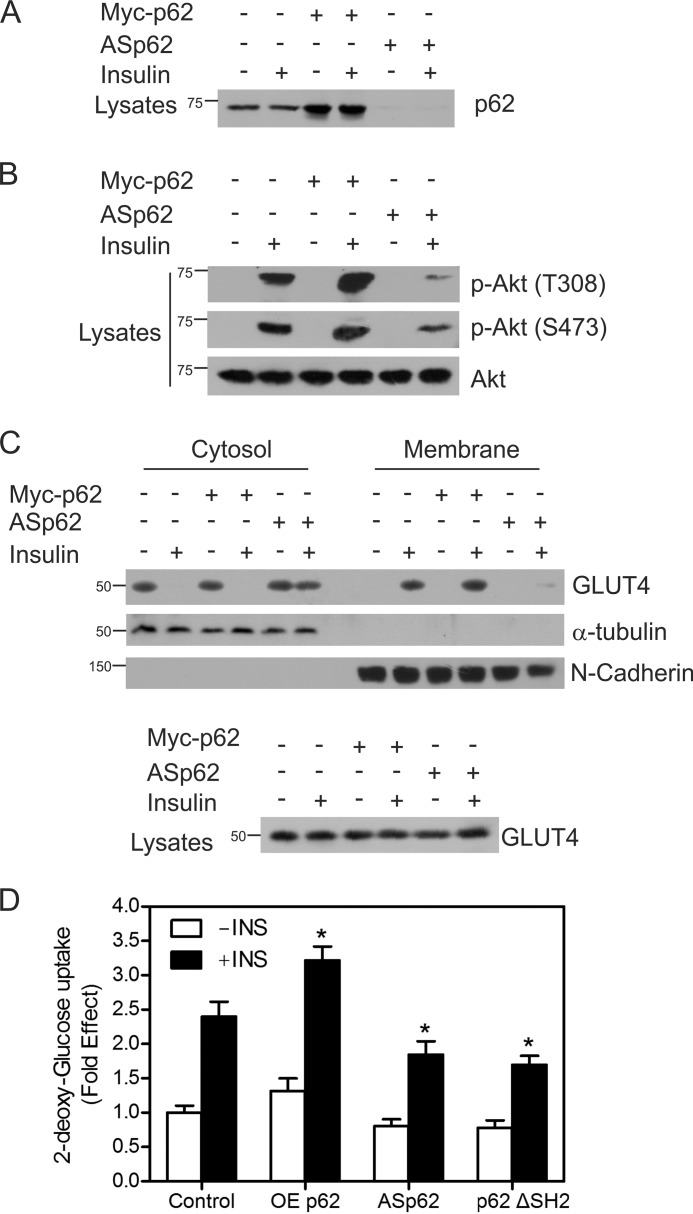
FIGURE 4.
p62 influences insulin receptor signaling. A, CHO/IR cells were transfected with either Myc-tagged p62 or ASp62. The transfected cells were treated with or without insulin (100 nm) for 15 min at 37 °C. Lysates from control and transfected cells were Western blotted with p62. B, the above lysates (A) were immunoblotted for phospho-Akt Thr-308 (p-Akt (T308)) and phospho-Akt Ser-473 (p-Akt (S473)) and total Akt (Akt). C, the transfected cells from above (A) were incubated in the presence or absence of insulin for 20 min, fractionated into membrane and cytosolic fractions, and Western blotted with GLUT4, α-tubulin, and N-cadherin. The lysates were immunoblotted for total GLUT4. D, OEp62, ASp62, or p62ΔSH2 mutants were expressed in CHO/IR cells, cells were stimulated in the presence or absence of 100 nm insulin for 20 min, and the rates of 2-deoxy-d-[3H]glucose uptake were determined. Each bar in the graph indicates the -fold change relative to the control cells unstimulated with insulin, which was taken to be 1. Differences from the control value treated with insulin and other groups are statistically significant (*, p < 0.001). Error bars indicate S.D.