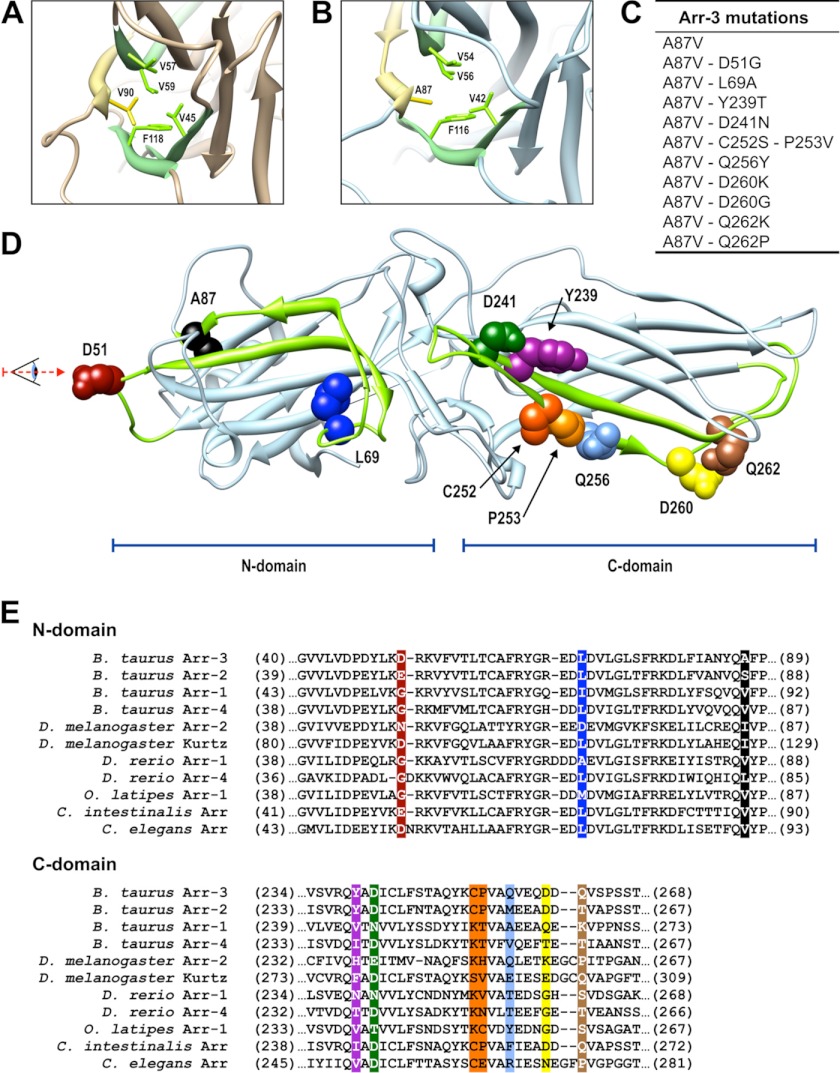
FIGURE 1.
Arrestin residues targeted in this study. A and B, crystal structure of arrestin-1 (Protein Data Bank entry 1CF1) (A) and arrestin-3 (Protein Data Bank entry 3P2D) (B), focusing on the core of the N-domain (viewed from the direction indicated in D). Side chains of Val-90 and Ala-87 (in arrestin-1 and -3, respectively) are shown in yellow, and adjacent hydrophobic residues are shown in green. C, arrestin-3 mutations introduced in this study. D, the receptor-binding surface of arrestin-3. Elements responsible for receptor preference are shown in green (β-strands V and IV in the N-domain and β-strands XV and XVI in the C-domain). The residues targeted in this study are shown as CPK models using the same color scheme as in E and in subsequent figures. E, sequence alignment of “receptor discriminator” elements of arrestins from different species (based on Ref. 9). Note that some of the homologous residues from other arrestins were introduced into arrestin-3 (C).