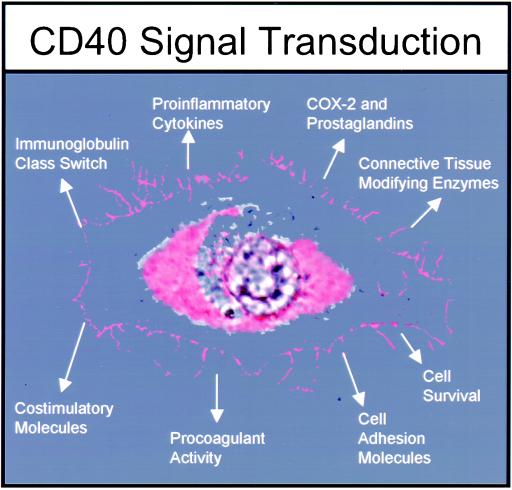
Figure 1.
Spectrum of activities induced after CD40 engagement on hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells. Unique to particular types of cells (e.g., lymphocytes, macrophages, and fibroblasts), CD40 engagement sets in motion a pattern of gene expression. The function of CD40 seems to be to “activate” a cell. For example, vascular endothelial cells after CD40 triggering produce cytokines such as IL-1 and IL-8, express cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and MMPs, and display an increased density of cell adhesion molecules. B lymphocytes depend on CD40 for survival, for expression of costimulatory molecules like B7 (to interact with T lymphocytes), and to undergo Ig class switching.