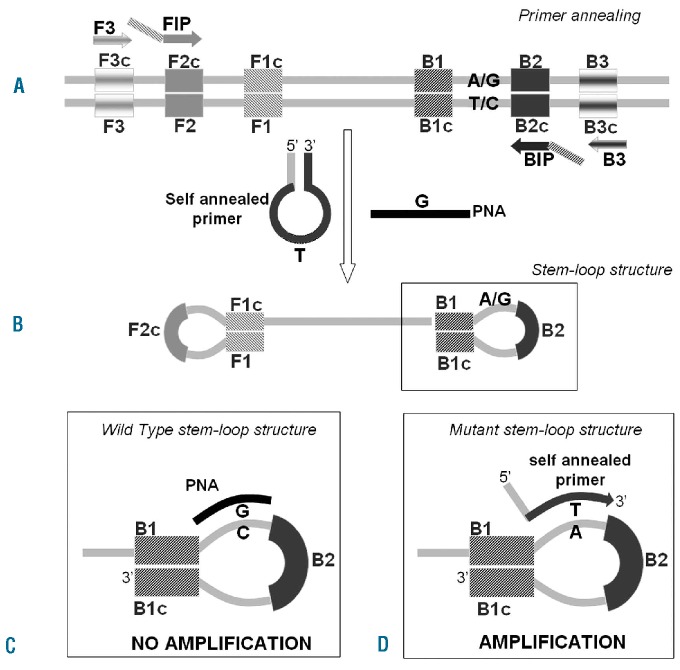
Figure 1.
The principle of AS-LAMP. (A) At a constant reaction temperature FIP and BIP are extended on the target DNA and the newly synthesized DNA chains are then displaced by extension of F3 and B3. (B) The displaced product generates a “stem-loop structure” which represents the starting structure for a LAMP reaction. (C) If the target in the reaction is wild-type, the peptide nucleic acid (PNA) forms a stable duplex with the stem-loop structure, preventing the annealing and extension of the mutant self-annealed primer and, therefore, suppressing the amplification. (D) If the target in solution is mutated, the PNA does not anneal, while the self-annealed primer breaks its internal interaction to bind its target and finally it is extended. The amplification can, therefore, proceed.