FIGURE 7.
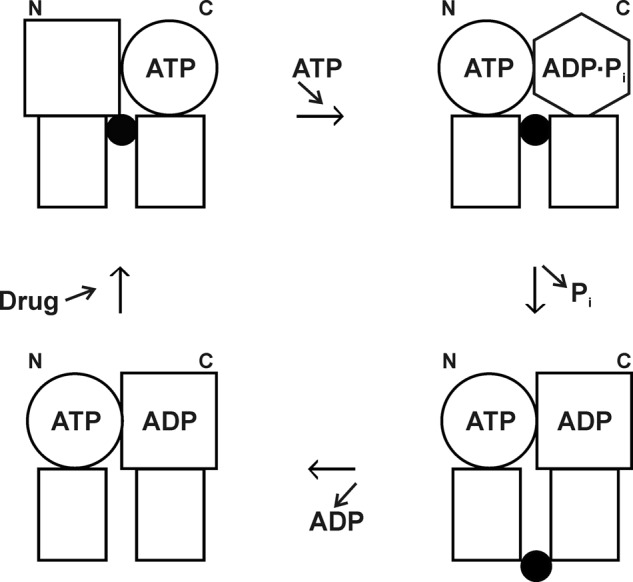
P-glycoprotein alternating sites mechanism. Rectangles, transmembrane domains; circles, squares, and hexagon, different conformations of the N- and C-terminal catalytic sites (NBDs); black circles, drug molecule. Binding of ATP to an empty N-terminal site (upper left) brings about hydrolysis of ATP in the C-terminal site (upper right). Relaxation of the C-terminal site drives drug from inward-facing higher affinity to outside-facing lower affinity (lower right) as Pi is released. Drug and ADP dissociate (lower left), and in the next cycle, it will be the C-terminal site that binds ATP and the N-terminal site that hydrolyzes it. This figure was reprinted from Ref. 75 with permission.
