FIGURE 8.
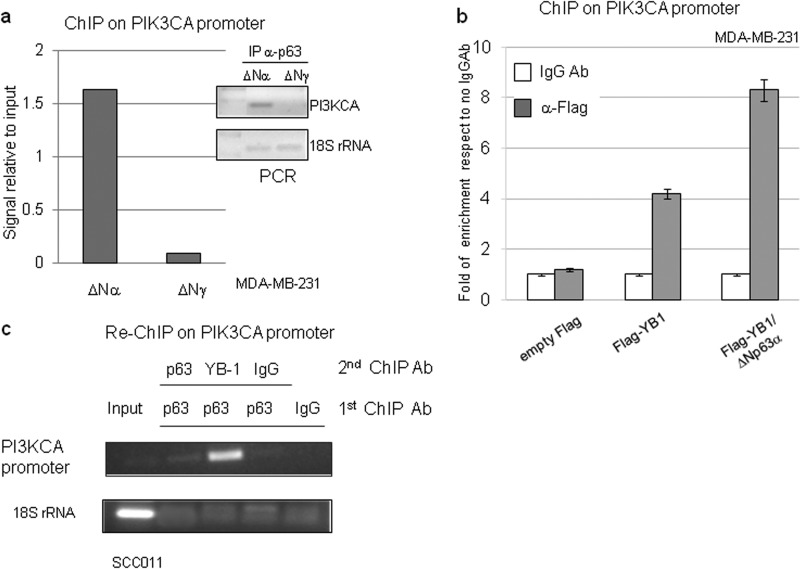
ΔNp63α increases YB-1 binding to the PIK3CA gene promoter. a, MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded at 60% confluency (1.2 × 106) in 100-mm dishes and transiently transfected with ΔNp63α or ΔNp63γ plasmid (5 μg). After formaldehyde cross-linking, the DNA-proteins complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-p63 (4A4) antibody. Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR-amplified with PIK3CA promoter oligonucleotides and 18 S rRNA oligonucleotides (right). The data obtained from the ChIP assay were measured by densitometry and are presented as signal relative to the input (left). b, MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded at 60% confluency (1.2 × 106) in 100-mm dishes and transiently transfected with 3×FLAG empty vector or 3×FLAG-YB-1 (5 μg) plasmid with or without ΔNp63α (2.5 μg) expression vector. The cells were cross-linked with formaldehyde, and DNA-protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody or irrelevant IgG antibody as negative control. The DNA immunoprecipitates were analyzed by quantitative PCR using PIK3CA or GAPDH promoter oligonucleotides. Quantitative RT-PCR results were analyzed with the ΔΔCT method and expressed as fold of enrichment with respect to the IgGAb control samples. Values are represented as the mean of three independent experiments. c, SCC011 cells at 85% confluency were fixed with formaldehyde, and the DNA-protein complexes were subjected to sequential ChIP with anti-p63 (4A4), anti-YB-1(Ab12148), or irrelevant IgG antibody as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR-amplified with PIK3CA promoter primers and 18 S rRNA primers to check the quality of the input chromatin and the cleaning of the other samples.