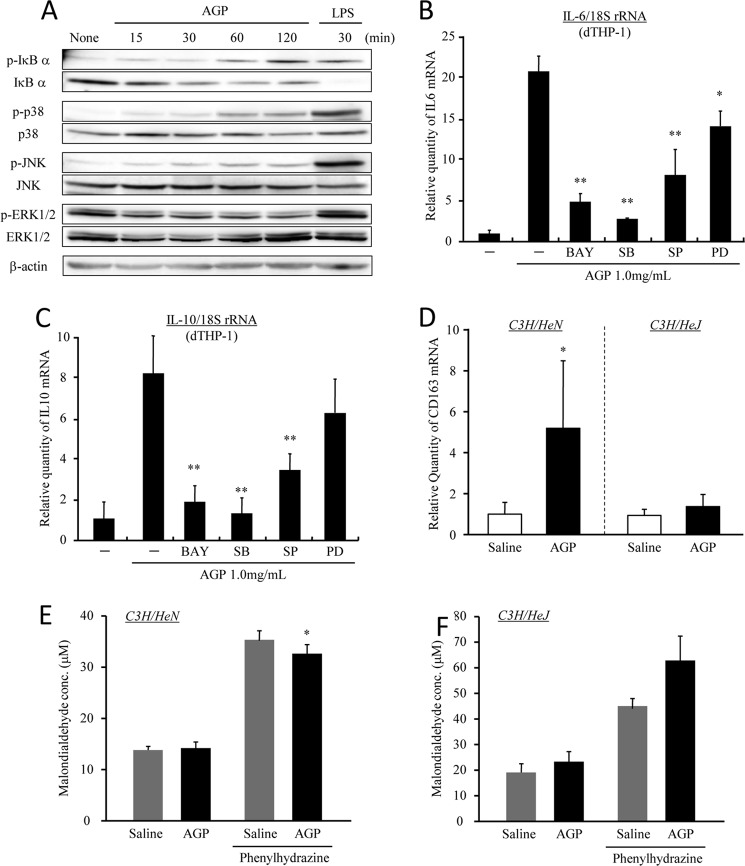
FIGURE 5.
AGP induces IL-6 and IL-10 via the activation of TLR4 signaling. A, dTHP-1 cells were treated with AGP or LPS each time. Cells were lysed, and Western blotting was performed using each of the indicated antibodies. B and C, dTHP-1 cells were pretreated with BAY11-7082 (1 nm), SB203580 (1.0 nm), SP600125 (1.0 nm), and PD98059 (10 nm) for 1 h and subsequently incubated with AGP (1 mg/ml) for 2 h. The expression levels of IL-6 (B) and IL-10 (C) were evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR. D–F, C3H/HeN and C3H/HeJ mice were intravenously injected with saline or AGP (5 mg/100 μl saline/animal), and phenylhydrazine was subsequently administered by intraperitoneal injection after 48 h. At 24 h after the phenylhydrazine administration, liver and blood were collected. The expression of CD163 (D) in the liver was evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR. Oxidative stress in plasma from C3H/HeN (E) and C3H/HeJ (F) mice was measured by means of a TBARS assay. Results are the means ± S.D. of six separate experiments. Statistically significant reduction was compared with AGP (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05).