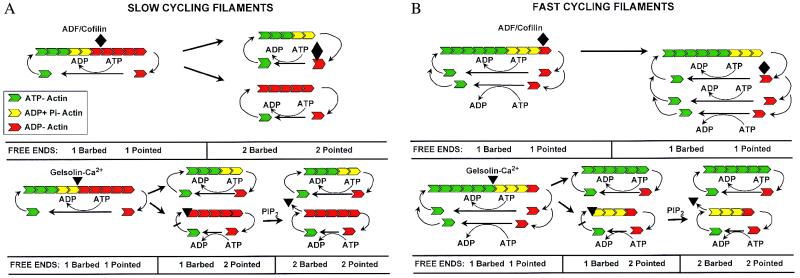
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of actin-filament cycling before and after addition of ADF/cofilin or gelsolin-Ca2+. (A) Actin filaments have a barbed and pointed end, as demonstrated by electron micrographs of myosin head-decorated actin filaments. The myosin heads bind at a 45° angle, defining a pointed and barbed end. The barbed end has a higher affinity for actin monomers and has a more rapid exchange rate than the pointed end. At steady state (Left), actin monomers come on the filament at the barbed end as ATP actin monomers (solid green). As they enter the filament, the ATP is hydrolyzed, forming an intermediate ADP + Pi (yellow) and then ADP-actin (red). ADP- actin has a much lower affinity for filament ends (Kd of approximately 6 μM) than ATP actin (Kd of 0.03 to 0.1 μM for the barbed end). Once the ADP-actin monomer dissociates from the pointed end, ATP is exchanged for ADP, and the actin monomer can again add to the barbed end [when ADF is bound to ADP-actin, profilin is required for this exchange to occur efficiently (3)]. This process is called treadmilling, because an individual monomer adds to the barbed end, cycles through the filament, and then dissociates from the pointed end. Treadmilling allows remodeling of actin filaments. The rate of remodeling depends on the number of free filament ends. Doubling the number of free ends of the same concentration of filamentous actin would be expected to double the rate of treadmilling (i.e., the identical concentration of actin existing as short filaments would be expected to recycle more rapidly than a population of long filaments). In the slow-cycling filament, significant amounts of ADP-actin exist in the filament; therefore, ADF/cofilin can bind and sever. Each time ADF severs, it doubles the filament ends. Gelsolin-Ca2+ has very high affinity for filaments and rapidly severs them. Because gelsolin also binds and caps the barbed ends, severing and capping doubles the free pointed ends but does not increase the free barbed ends. However, when chemotactic signal transduction pathways increase the concentration of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate, gelsolin will dissociate from the barbed end, and the number of free barbed ends will double. (B) When actin filaments rapidly cycle, there is reduced time for ATP hydrolysis, and the filament would be expected to have a lower content of ADP-actin. This condition would be expected to reduce the ability of ADF/cofilin to bind to the filament and thus reduce its ability to sever and increase the number of free ends. Therefore, ADF/cofilin would lose its ability to enhance treadmilling. However, gelsolin-calcium, by virtue of its high-affinity binding, would be expected to continue to bind and sever filaments with low ADP content and therefore continue to be effective at increasing the number of filament ends. Space does not permit illustration of exchange of the two actin monomers per filament after gelsolin severing (Bottom Right).