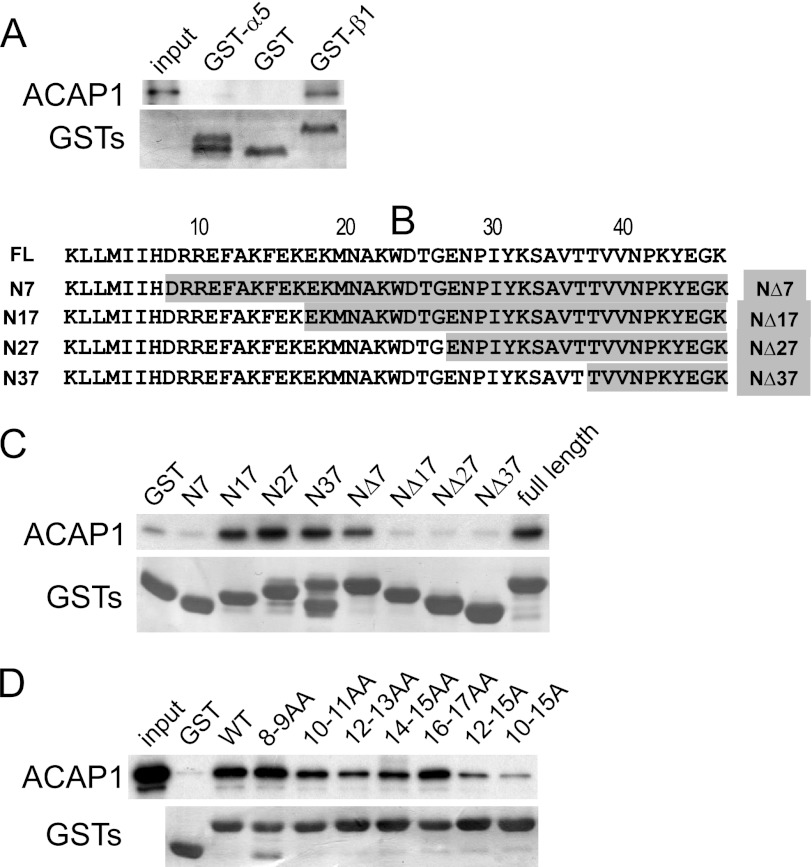
FIGURE 1.
Identifying a sequence in integrin β1 critical for its direct binding to ACAP1. A, ACAP1 binds directly to the cytoplasmic domain of integrin β1. The cytoplasmic domain of either α5 or β1 was fused to GST, and the resulting fusion proteins were bound to beads for incubation with soluble ACAP1 in pulldown experiments. B, truncation mutants of the cytoplasmic domain of integrin β1. Residues are numbered from the membrane-proximal end. FL, full-length ACAP1. C, identifying a region in the cytoplasmic domain of β1 responsible for its direct binding to ACAP1. Different truncations of β1 as GST fusion proteins were bound to beads for incubation with full-length ACAP1 as soluble recombinant protein in pulldown experiments. Beads were immunoblotted for ACAP1 and Coomassie Blue-stained for GST fusion proteins. D, alanine-scanning mutagenesis identifies specific residues within the cytoplasmic domain of β1 responsible for its direct binding to ACAP1. Residues within the cytoplasmic domain of β1 were mutated to alanines as indicated. The mutants as GST fusion proteins were then bound to beads for incubation with soluble ACAP1 in pulldown experiments. Beads were immunoblotted for ACAP1 and Coomassie Blue-stained for GST.