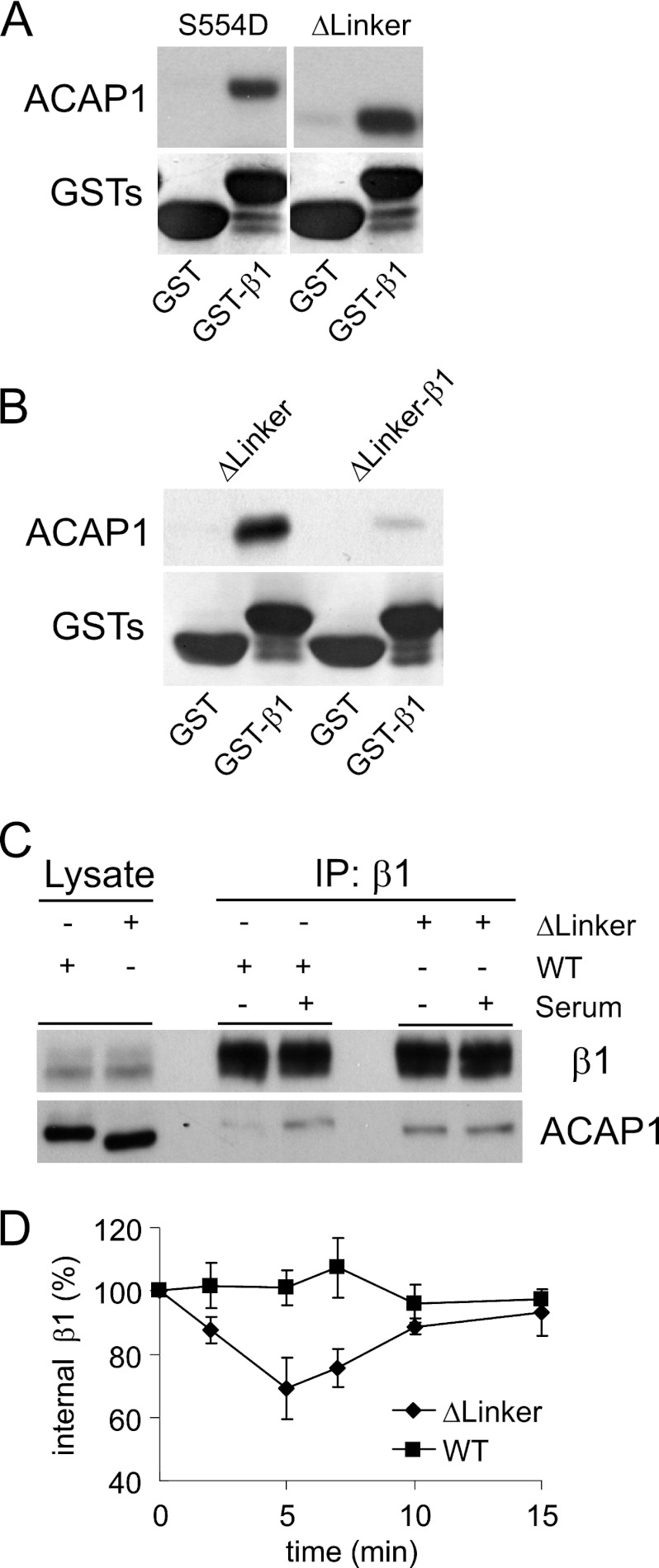
FIGURE 7.
Linker region inhibits cargo binding. A, excision of the linker region results in enhanced cargo binding by ACAP1 in vitro. The different forms of ACAP1 were incubated with GST-β1 in a pulldown experiment. B, fusion of the β1 peptide to the linker mutant prevents the resulting fusion construct from binding intermolecularly to the same cargo peptide on beads in a pulldown assay. The fusion construct was compared with the non-fusion counterpart in binding to GST-β1 in a pulldown experiment. The input shows proteins stained with Coomassie Blue, whereas pulldown results were immunoblotted for the proteins indicated. C, excision of the linker regions results in enhanced cargo binding by ACAP1 in vivo. ACAP1 (either wild-type or with the linker region excised) was expressed in HeLa cells. The association of endosomal β1 with either form of ACAP1 was then assessed through co-precipitation (IP). D, excision of the linker region induces β1 recycling under basal (no stimulation) conditions. The integrin recycling assay was performed under basal conditions on HeLa cells that stably expressed either wild-type or mutant (with the linker region deleted) ACAP1. The mean ± S.E. from three experiments is shown.