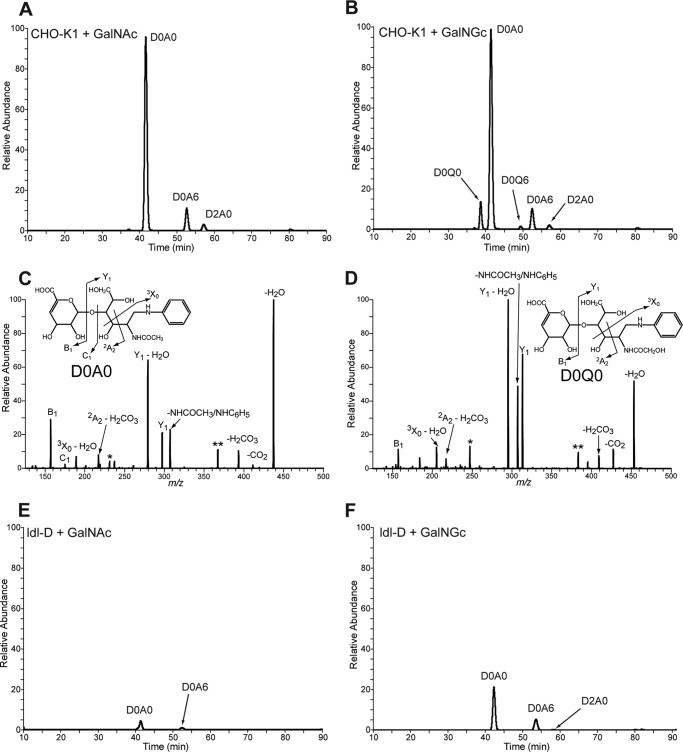
FIGURE 7.
Disaccharide analysis of heparan sulfate extracted from wild type and mutant CHO cells after feeding GalNGc or GalNAc. Wild type CHO-K1 and ldl-D cells were kept under Neu5Gc-free conditions and supplemented with 10 mm GalNGc or 10 mm GalNAc for the last 3 days before cells reach confluence. Heparan sulfate from the medium of both wild type CHO-K1 and ldl-D cells was enzymatically depolymerized and subjected to compositional disaccharide analysis by GRIL-LC/MS. The extracted ion current for internal disaccharide containing both GalNGc and GalNAc is shown for each cell line and feeding condition. Peak assignments for N-acetylated species were made based on co-elution with differentially stable isotope-labeled standards added to each sample. A, extracted ion current chromatograph for wild type CHO-K1 cells fed GalNAc. B, extracted ion current chromatograph for wild type CHO-K1 cells fed GalNGc. C and D, tandem mass spectra of D0A0 and D0Q0 in heparan sulfate from GalNGc fed CHO cells. The daughter ion profiles of both the D0A0 in GalNAc fed CHO-K1 cells (C) and the putative D0Q0 detected in GalNGc fed CHO-K1 cells (D) were compared. The overall CID spectrum of the putative D0Q0 ion is most similar to that of D0A0, suggesting that it is structurally similar and consistent with its assignment as D0Q0 and not another isobaric species. Both spectra show three product ions with identical m/z values consistent with the B1, C1, and 2A2 ions from the nonreducing end (see insets). All of the remaining product ions found in D0A0 have corresponding product ions in D0Q0 that differ by 16 mass units expected for species that differ only in the substitution of an N-glycolyl group for an N-acetyl group. E, extracted ion current chromatograph for ldl-D cells fed GalNAc. F, extracted ion current chromatograph for ldl-D cells fed GalNGc. Species marked in CID spectra with single and double asterisks are corresponding undefined daughter ions that differ by 16 amu.