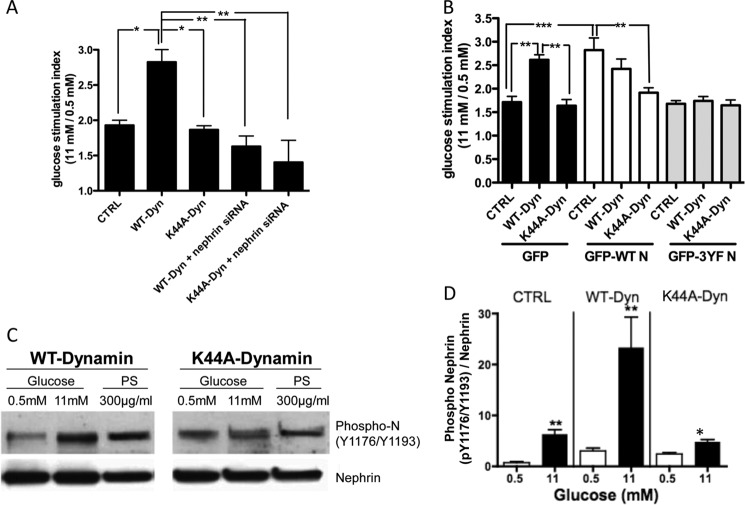
FIGURE 3.
Nephrin mediates the positive effect of Dynamin on insulin secretion. A, regular MIN6 cells that in contrast to MIN6-C3 express endogenous Nephrin were infected with WT-Dynamin or K44A-Dynamin mutants in the presence or absence of Nephrin siRNA. When Nephrin siRNA was present, the effect of Dynamin on insulin secretion was abolished. Likewise, no GSIR was observed in K44A-Dynamin-overexpressing cells in the presence of Nephrin siRNA. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, n = 4. B, MIN6 cells stably transfected with either empty vector control (CTRL), WT-Nephrin, or 3YF-Nephrin were infected with Dynamin constructs (WT-Dynamin or K44A-Dynamin). Glucose stimulation indices demonstrated that WT-Dynamin did not further augment the stimulation index observed in WT-Nephrin-overexpressing cells. In addition, the positive effect of WT-Dynamin on GSIR was completely abolished in 3YF-Nephrin-overexpressing cells. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. C, Nephrin phosphorylation was determined in WT-Dynamin- and K44A-Dynamin-infected cells. Overexpression of K44A-Dynamin abolished the ability of glucose and PS to stimulate Nephrin phosphorylation. D, quantitative bar graph analysis of Nephrin phosphorylation in control cells (CTRL), WT-Dynamin-overexpressing cells (WT-Dyn), and K44A-Dynamin-overexpressing cells (K44A-Dyn) cultured in 0.5 or 11 mm glucose. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, n = 4.