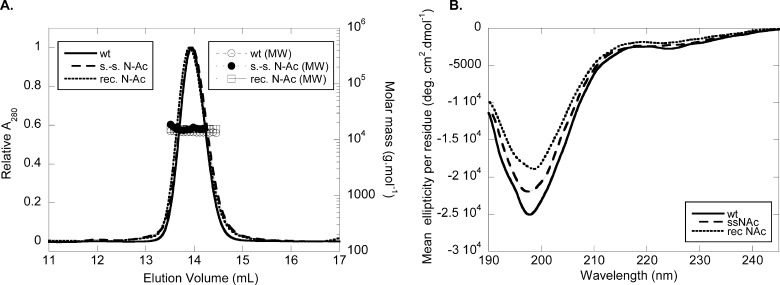
FIGURE 2.
Biophysical characterization of Nα-acetylated α-syn. A, gel-filtration/light scattering analysis. Purified lyophilized WT and N-Ac α-syn were diluted to 30 μm in gel-filtration buffer (50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mm NaCl, 0.05% w/v NaN3) and filtered (0.22 μm). Samples (100 μl) were run at 0.4 ml/min on a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column connected with UV multiangle light scattering and differential refractive index detectors. Molar masses were calculated based on concentrations determined on line by differential refractometry (dn/dc = 0.185 ml/g). The left ordinate axis shows the elution pattern of WT (continuous line), semisynthetic (s.-s., dashed line), and recombinant (rec., dotted line) N-Ac α-syn. The right ordinate axis shows calculated molecular weights for WT (open circles), semisynthetic (s.-s., closed circles), and recombinant (rec., squares) N-Ac α-syn. B, circular dichroism spectra of WT (continuous line), semisynthetic (s.-s., dashed line), and recombinant (rec., dotted line) N-Ac α-syn. Proteins were dissolved to 10 μm in 20 mm sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 (without lipids), and analyzed in a 1-mm quartz cell.