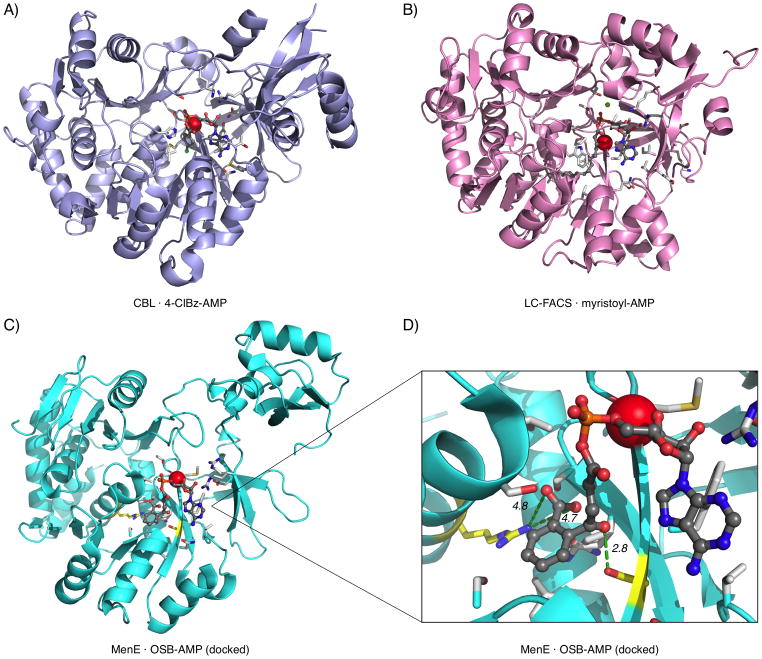
Figure 1.
Active sites of acyl-CoA synthetases. A) 4-Chlorobenzoate-CoA synthetase (CBL) with 4-chlorobenzoyl-AMP intermediate and substrate binding residues (PDB: 3CW8).[85] B) Long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (LC-FACS) with myristoyl-AMP intermediate and substrate binding residues (portions of structure not shown for clarity) (PDB: 1V26).[86] C) S. aureus MenE unliganded form with OSB-AMP docked in the putative active site (loop residues 280–284 not shown for clarity) (PDB: 3IPL).[87] D) Arg-222 and Ser-302 (yellow) and putative interactions with OSB aromatic carboxylate (4.7, 4.8 Å) and OSB ketone oxygen (2.8 Å), respectively (loop residues 280–284 not shown for clarity). Sidechains within 4 Å of ligands (white) and C-terminus of helix B3/4 (red sphere) are shown in each case.