Figure 6. Oncologic dose of zoledronic acid (ZOL) increases the percentage of necrotic and apoptotic osteocytes, and the area of alveolar bone devoid of basic fuchsin stain in mandibles of rice rats treated for 18 wks.
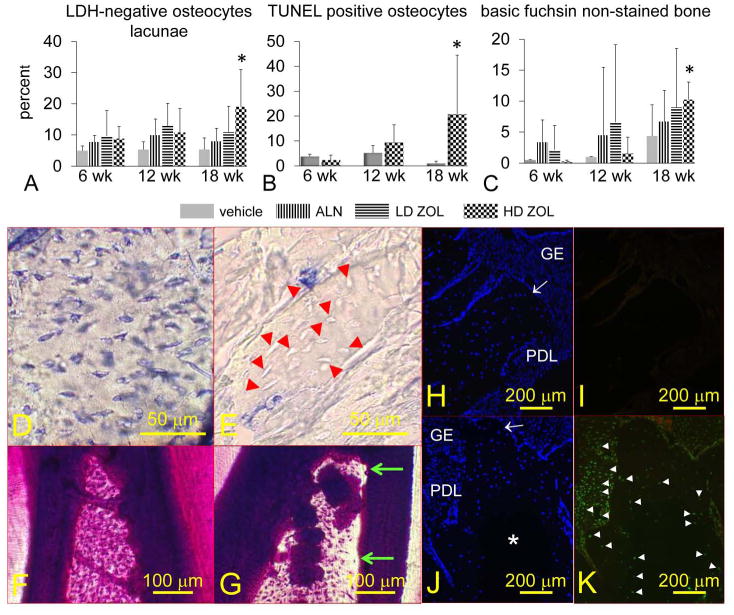
The percentage of osteocytes that do not show lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) expression (necrotic osteocytes) (A), TUNEL positive osteocytes (apoptotic) (B), and areas devoid of basic fuchsin stain (C) are shown. Rice rats were treated with vehicle, alendronate (ALN), and low (8 μg/kg) or high doses (80 μg/kg) of ZOL for 6, 12 and 18 wks. An asterisk denotes a significant difference from its respective time-matched vehicle-treated group (P < 0.05). Representative photos of mandibular alveolar bone histochemically stained for LDH in a rat treated with vehicle (D) or HD-ZOL (E) for 18 wks. Osteocytes that are blue-stained express LDH (viable). Osteocytes that are dead are unreactive (unstained). Most of the osteocytes present at the interdental alveolar bone in the mandibles of rice rats treated with vehicle are viable (D). In contrast, rats treated with HD-ZOL for 18 wks show extensive areas of alveolar bone containing empty osteocyte lacunae or lacunae with unstained osteocytes (E) (red arrowheads). En bloc basic fuchsin stained mandibles at the interdental alveolar bone of a rat treated with vehicle (F) or HD-ZOL for 18 wks (G). Note areas devoid of basic fuchsin stain at the coronal region of the interdental alveolar bone in the rat treated with ZOL (green arrows). Photos depicting DAPI (H, J) and TUNEL (I, K) staining in mandibles from vehicle and HD-ZOL treated rats for 18 wks, respectively. Gingival epithelium (GE), periodontal ligament (PDL), alveolar bone crest (white arrow). DAPI positive cells are stained blue (H, J). Note a big area in the center of the alveolar bone that is devoid of DAPI reaction in a rat treated with HD-ZOL (J) compared to a more uniform DAPI reaction in a vehicle-treated rat (H). Note the TUNEL-positive reaction (white arrowheads) in osteocytes adjacent to the DAPI negative area, and in many cells of the periodontal ligament area in a rat treated with ZOL for 18 wks (K). In contrast no TUNEL-positive reaction is observed in the mandible of the vehicle-treated rat (I). Bars = 50 μm (D, E), 100 μm (F, G), and 200 μm (H-K), respectively.
