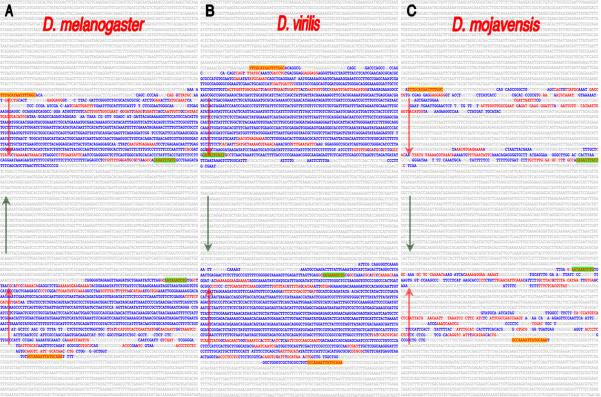
Fig. 3.
Intra-genomic alignments revealed an inve rted repeat that is present once in each of the Drosophila genomes and located upstream of the cas transcribed sequence. Shown are the inverted repeats within the D.melanogaster (A), D.virilis (B) and D.mojavensis (C) cas orthologous sequences. Uppercase blue- and red-colored sequences are identical (but inverted) within the repeats. The red-typeface sequences highlight CSBs that are common among the different orthologous regions in the repeat sequences and the yellow and green highlighted CSBs identify the outer-most repeat sequence blocks present in all species (orientation of the repeats is illustrated by the arrows). The repeats were initially identified via the EvoPrinter repeat finder program and their inverted orientation revealed by subsequent composite eBLAT analysis. The D. melanogaster inverted repeat extends from position -0.68 to -4.31 kb above the predicted cas transcription start site. Note the species-specific differences in the length and extent of sequence identity between the inverted halves. Conserved sequences flanking the inverted repeats are not highlighted.