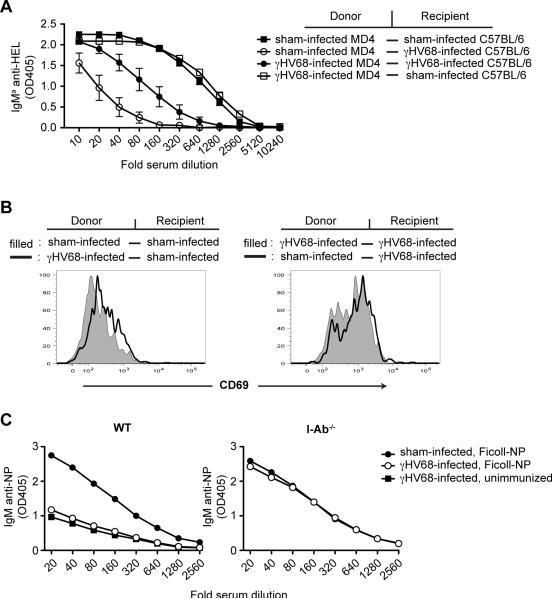
Figure 4. Suppression of antibody responses in caused by the environment in the infected host.
A) MD4 and C57BL/6 mice were infected with γHV68 or sham infected. Six days later B cells from γHV68-infected or sham-infected MD4 mice were purified and adoptively transferred into γHV68-infected or sham-infected C57BL/6 mice by i.v. injection. All mice also received CD4+ T cells isolated from mice primed 4 days earlier with SRBC. At the time of transfer the mice were immunized with 100μl 10% SRBCHEL by i.p. injection. Seven days later serum was collected and the IgMa anti-HEL response was determined by ELISA (n=5/ group). B) Isolated B cells from mice infected 8 days earlier or from sham-infected mice were CFSE labeled and adoptively transferred into γHV68-infected or sham-infected C57BL/6 mice. Sixteen hours later spleens were collected and the CD69 expression was determined on B220+ CFSE+ cells (n=4/ group). Representative histograms are shown. C) C57BL/6 and I-Ab−/− mice (n=5/ group) were infected with γHV68 or sham infected. Seven days later the mice were immunized with Ficoll-NP or left unimmunized. After seven days blood was collected and the IgM anti-NP response was determined by ELISA. Error bars show SEM. All data is representative of at least 2 independent experiments.