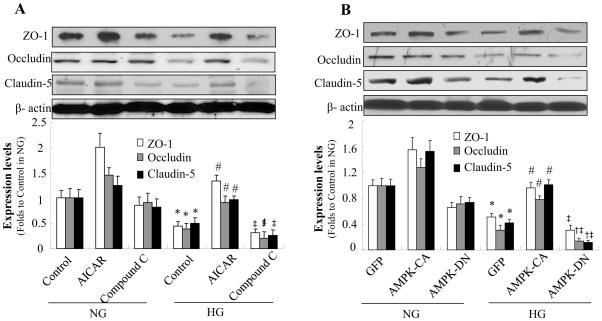
Figure 6. AMPK activation prevents high glucose-induced loss of tight junction proteins.
Confluent HBMECs were exposed to HG for 72 h. A: HG decreased expression of zonula occludens (ZO)-1, occludin, and claudin-5. Tight junction protein levels were increased by AICAR (0.5 mmol/l) and further decreased by compound C (10 μmol/l). *P < 0.05 for con/HG vs. con/NG; #P < 0.05 for AICAR/HG vs. con/HG; ‡ P < 0.05 for Compound C/HG vs. AICAR/HG, n=3. B: Degradation of zonula occludens (ZO)-1, occludin, and claudin-5 under HG conditions was reversed by overexpression of constitutively active AMPK (AMPK-CA) and enhanced by overexpression of dominant negative AMPK (AMPK-DN). *P < 0.05 for GFP/HG vs. GFP/NG; #P < 0.05 for AMPK-CA/HG vs. GFP/HG; †P < 0.05 for AMPK-DN/HG vs. GFP/HG; ‡P < 0.05 for AMPK-DN/HG vs. AMPK-CA/HG, n=3. β-actin was used as a control for protein loading. The blot is a representative of three blots from three independent experiments. NG: 5 mmol/l D-glucose; HG: 25 mmol/l D-glucose.