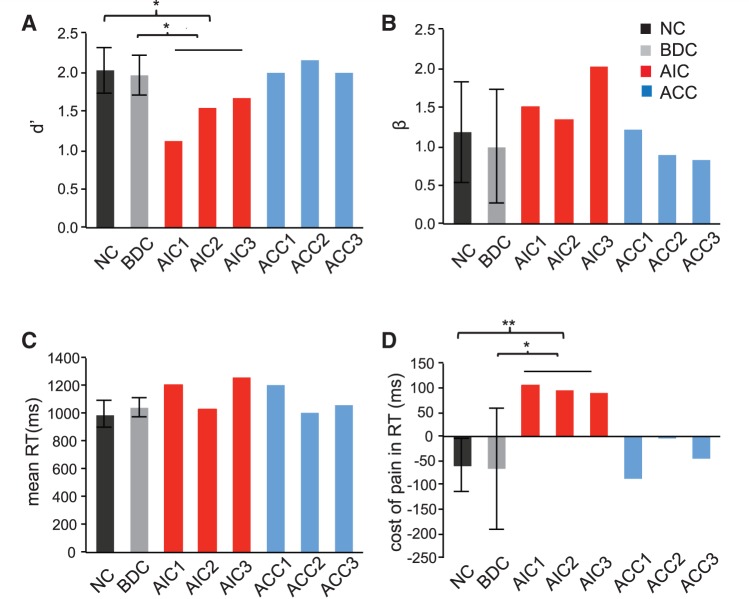
Figure 3.
Behavioural performance on task pain (TP). (A) Patients with anterior insular cortex (AIC) lesions (P < 0.05), but not anterior cingulate cortex patients (P > 0.05), had significantly smaller d′ compared with neurologically intact controls and brain-damaged controls, indicating impaired discrimination accuracy to empathetic pain in anterior insular cortex patients. (B) Neither patients with anterior insular cortex lesions nor those with anterior cingulate cortex lesions showed any significant alternation in decision bias indexed by β during task pain (P > 0.05). (C) Neither patients with anterior insular cortex lesions nor anterior cingulate cortex lesions showed any significant alternation in overall reaction time (RT) [(RTTP-pain + RTTP-no pain)/2] (P > 0.05). (D) Patients with anterior insular cortex lesions (P < 0.01 versus neurologically intact controls and P < 0.05 versus brain-damaged controls), but not those with anterior cingulate cortex lesions (P > 0.05), had greater cost of pain (RTTL-pain – RTTL-no pain). Error bar represents 95% confidence interval (CI). Statistical inference was not based on 95% confidence interval but on the bootstrapping method. All reaction times were calculated based on correct trials only. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.