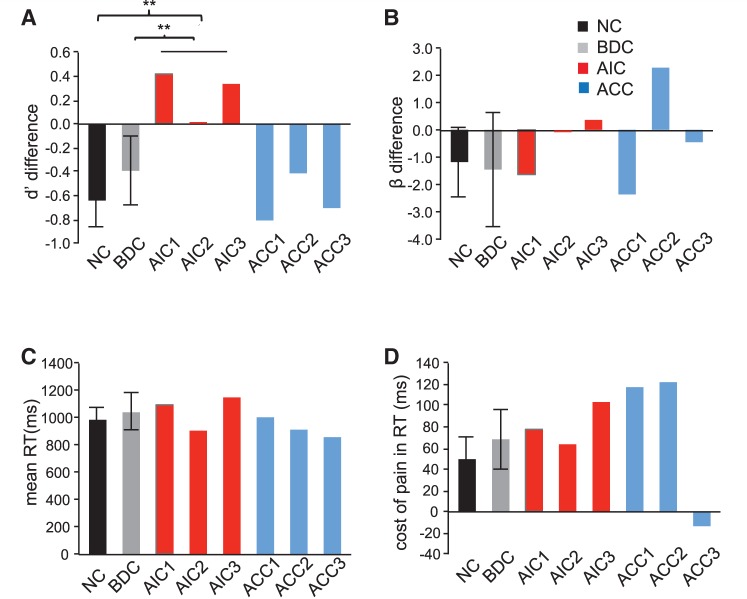
Figure 4.
Behavioural performance on task laterality (TL). (A) Patients with anterior insular cortex lesions (P < 0.01), but not those with anterior cingulate cortex lesion patients (P > 0.05), lacked the normal interference effect of pain on laterality discriminability. (B) Neither patients with anterior insular cortex lesions nor those with anterior cingulate cortex lesions showed significant difference in interference effect of pain on task laterality decision bias (P > 0.05). (C) Neither the anterior insular cortex lesions nor the anterior cingulate cortex lesions showed any significant alternation during laterality judgment in overall reaction time (RT) of task laterality (TL) [(RTTL-pain + RTTL-no pain)/2] (P > 0.05). (D) Neither patients with anterior insular cortex lesions nor those with anterior cingulate cortex lesions showed significant differences in RT cost of pain during TL (RTTL-pain − RTTL-no pain) (P > 0.05). Error bar represents 95% confidence interval. Statistical inference was not based on 95% confidence interval but on the bootstrapping method. All RTs were calculated based on correct trials only. **P < 0.01.