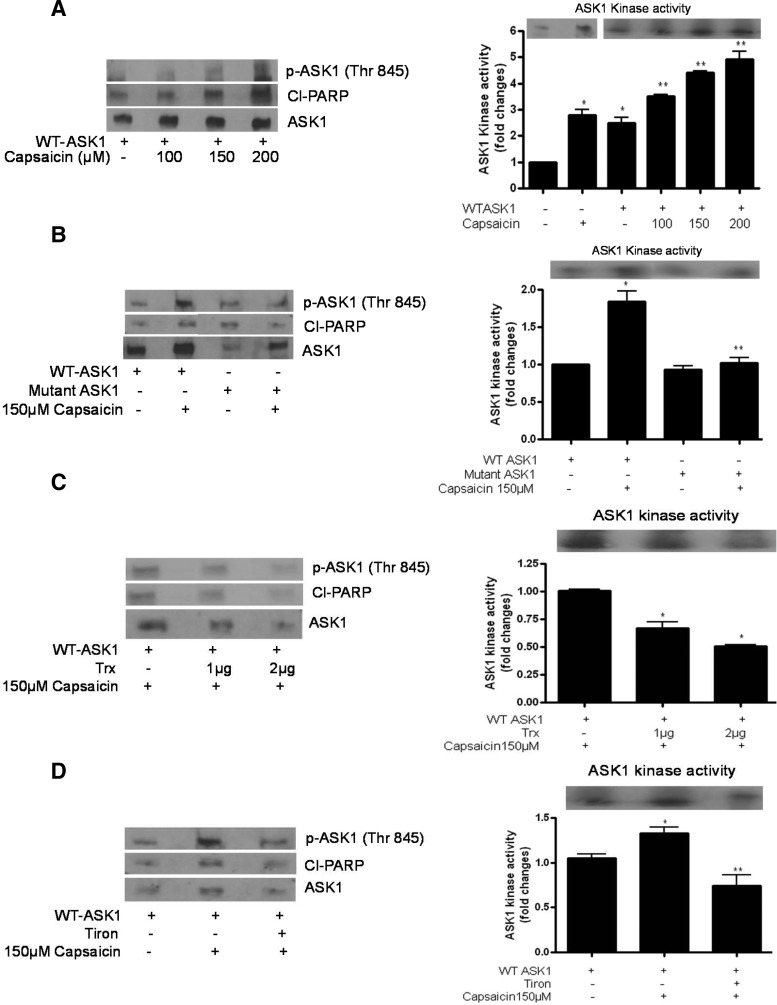
FIG. 4.
Effect of capsaicin on ASK1 kinase activity. AsPC-1 cells were transiently transfected with (A) HA-tagged WT-ASK1 (2 μg) or (B) HA-tagged WT-ASK1 and HA-tagged mutant ASK1 (2 μg) or (C) HA-tagged WT-ASK1 (2 μg) and Flag-tagged Trx (1 μg or 2 μg) or (D) HA-tagged WT-ASK1 expression plasmid followed by 1 h treatment with 10 mM tiron. Transfected cells were treated with DMSO or 150 μM of capsaicin for 24 h. Kinase activity of ASK1 was determined by the immune complex-coupled kinase assay using myelin basic protein (MBP) as a direct substrate and 0.5 μCi of [γ32P] ATP. MBP phosphorylation was detected using autoradiography. To determine phosphorylation of ASK1 and apoptosis in the same sample, the upper part of the membrane (>50 kDa) was cut out and immunoblotted with anti-p-ASK-1 (Thr 845) and Cl-PARP antibody. Bar diagram shows the quantitation of ASK1 kinase activity. These experiments were performed three times independently with similar observations made in each experiment. Values are means±SD of three individual experiments. *Statistically different when compared with control (p<0.05) and **statistically different when compared with capsaicin treatment between mutant ASK1 and WT-ASK1 treatment or WT-ASK1 with capsaicin treatment (p<0.05), as analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post-hoc test.