Fig. 6.
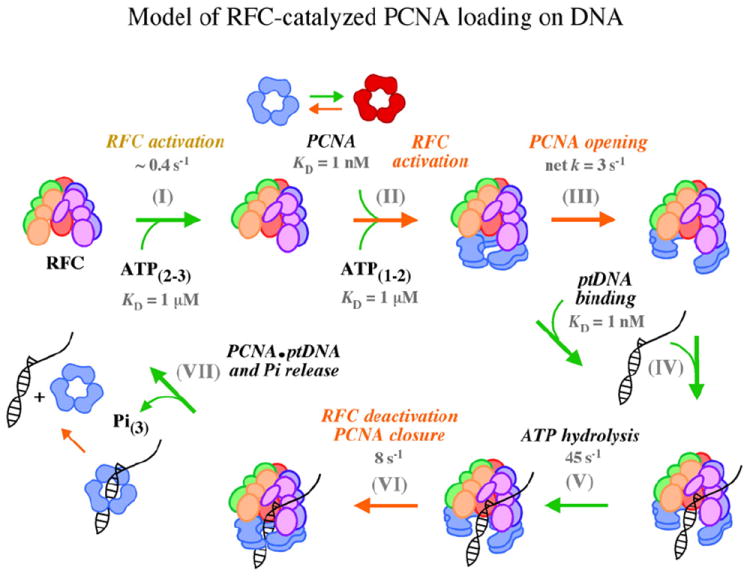
A model pathway for RFC-catalyzed PCNA loading on ptDNA. The schematic depicts key steps in the clamp loading reaction determined thus far. (I) Binding of two to three ATP molecules to RFC is followed by (II) RFC interaction with PCNA, additional binding of one to two ATP molecules,20 and slow activation steps involving conformational changes in RFC and PCNA that (III) lead to a stable open-clamp complex. (IV) ptDNA binds rapidly and with high affinity to activated RFC·ATP·PCNA complexes, (V) triggering ATP hydrolysis. (VI) Next, another slow step involving conformational changes in RFC and PCNA leads to closure of the clamp around ptDNA, (VII) release of products (Pi, PCNA·ptDNA), and catalytic turnover. Under the conditions of our in vitro experiments, slow dissociation of PCNA·ptDNA may contribute to the turnover rate (slow steps are indicated by orange arrows). The proposed partitioning of PCNA between loading-active and loading-inactive forms is also shown.
