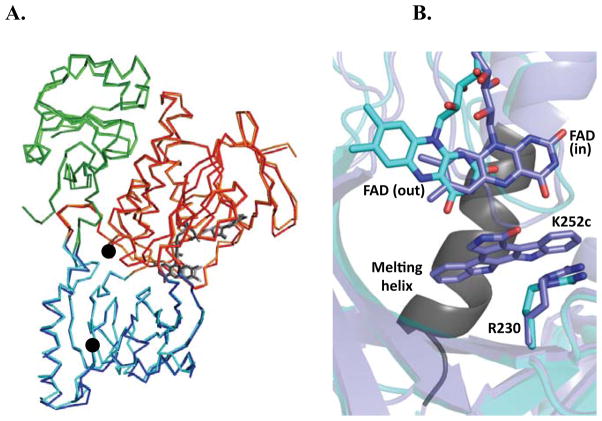
Figure 2.
Overall structure of RebC-10x aligned with wild type RebC. (A) RebC (lighter colors) and RebC-10x (darker colors) are aligned, showing the FAD binding domain (red), substrate binding domain (blue), thioredoxin-like domain (green), and FAD (grey sticks). RMSD of mainchain atoms is 0.46 Å. See Fig. S5 for comparison of (B) RebC-10x shows retention of the ‘mobile flavin’, where flavin binds in the ‘out’ position of native RebC-10x (cyan) and in the ‘in’ position when product is bound (slate), and the ‘melting helix’, where residues 354–363 (black) become disordered in absence of a bound indolocarbazole ligand (melting helix termini are marked with black circles in (A)). Arg230 is labeled to help relate this view of the active site with those shown in Fig. 3 and S6.