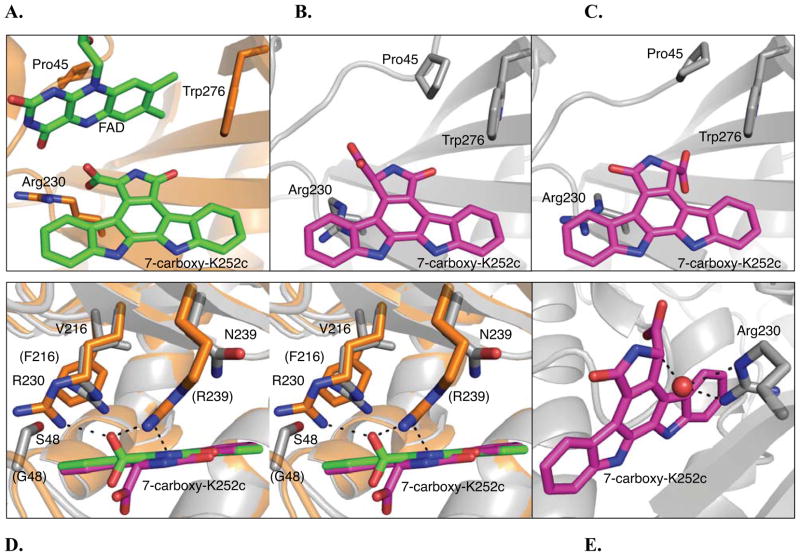
Figure 3.
RebC and RebC-10x substrate binding pocket. (A) RebC substrate binding pocket (PDB ID 2R0G) with protein backbone shown in orange and cofactor, FAD, and substrate, enol 7-carboxy-K252c, carbons in green and in stick representation. The sidechains, Arg230, Pro45, and Trp276 (representing a hydrophobic region of the binding pocket) are also shown in stick representation. (B) The S-keto form of 7-carboxy-K252c as found in molecule A of the RebC-10x CPA soaked crystal. Protein carbons are colored grey and substrate shown in stick representation and carbons colored magenta. The carboxyl group of substrate is proximal to Arg230, as in RebC. (C) The alternate orientation of substrate, as found in molecule B of the RebC-10x CPA soaked crystal. The carboxyl group of substrate is proximal to Trp276; coloring as in (B). (D) A stereo representation of an overlay of the RebC and RebC-10x (molecule A) active sites, shown from above. Substrate and protein colors the same as (A) – (C); RebC sidechains are labeled in parentheses. (E) A water molecule (red sphere) present in RebC-10x structure is located 2.6, 3.1 and 3.1 Å from two nitrogens of Arg230 and the C-7 position of 7-carboxy-K252c, respectively. In all stick representations, oxygen is shown in red and nitrogen in blue (see Figure S8A for the water binding site in the alternative orientation of substrate). See also Figure S7.