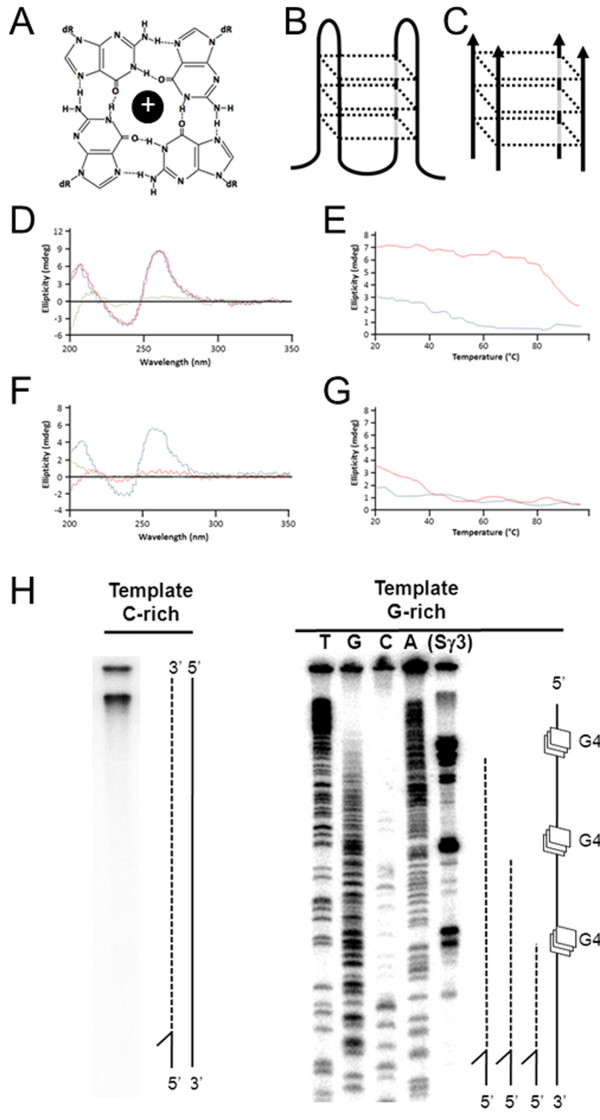
Figure 1 .
Formation of G4 DNA structures. (A) Illustration of guanine quartet with each guanine engaged in four hydrogen bonds and a central metallic cation. (B) Structural illustration depicting a unimolecular antiparallel G4 DNA. (C) Structural illustration depicting an intermolecular parallel G4 formed from guanine rich strands of DNA. (D) CD spectrum of TP DNA 49-mer in 50 mM KCl (blue line 25°C, red line 37°C, green line 95°C). (E) Melting curve of TP DNA 49-mer molar ellipticity at 263 nm in 50 mM KCl (red line) or 50 mM LiCl (blue line). (F,G) As in D,E but TP DNA 49-mer was not pre-folded into G4. (H) Primer extension reactions using Klenow fragment and single stranded phagemid template corresponding to the C-rich strand of Sγ3 from pCR2.1-C (left) or the G-rich strand of Sγ3 from pCR2.1-G (right) resolved by denaturing PAGE. Modeled to the right of each image are polymerase extensions (dotted line) on template (solid line) or with G4 sites (squares). Stall sites for G-rich pCR2.1-G map to guanine repeats, determined by cycle di-deoxy sequencing of the G-rich template strand using the extension reaction primer.