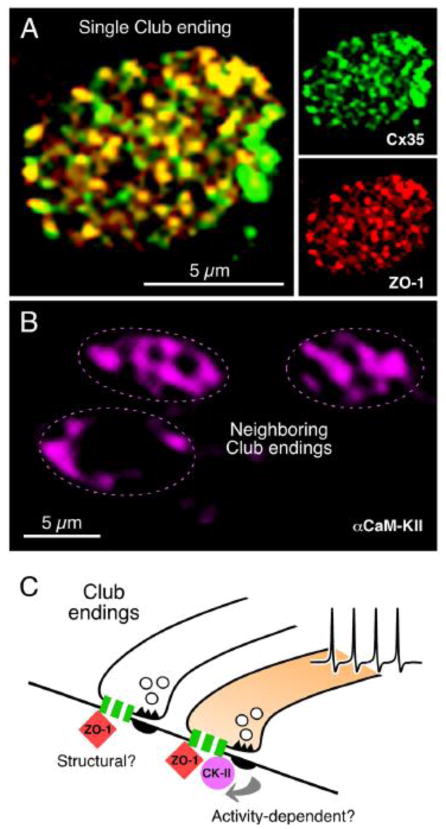
FIGURE 10. Connexin-associated proteins in electrical synapses.
A, Cx35 and ZO-1 co-localize at Club Endings. Laser scanning confocal projection of an individual Club ending after double immunolabeling showing intense punctate labeling for Cx35 and ZO-1 (right panels) and high levels of co-localization in yellow (left panel). C, In contrast, αCaMKII labeling is more diffuse and highly variable between contiguous Club endings. While αCaMKII labeling was always observed at the periphery, where PSDs are located, it is also found at the center of the Club endings contact area in some cases (compare top Club endings with the bottom one). D, The extensive co-localization of Cx35 with ZO-1 suggests that this scaffold protein could constitute a structural component of gap junctions at these terminals. Activity of neighboring chemically transmitting regions within the terminal trigger changes in junctional conductance, via a PSD-mediated mechanism (arrows) promoting the association of CaMKII to Cx35 and ZO-1. The association of CaMKII to electrical synapses would be thus non-obligatory and driven by synaptic activity. For convenience, as simplified gap junction is illustrated; the cartoon does not indicate that association is exclusively pre- or postsynaptic. Modified from Flores et al., 2010 [120].