Fig. 2.
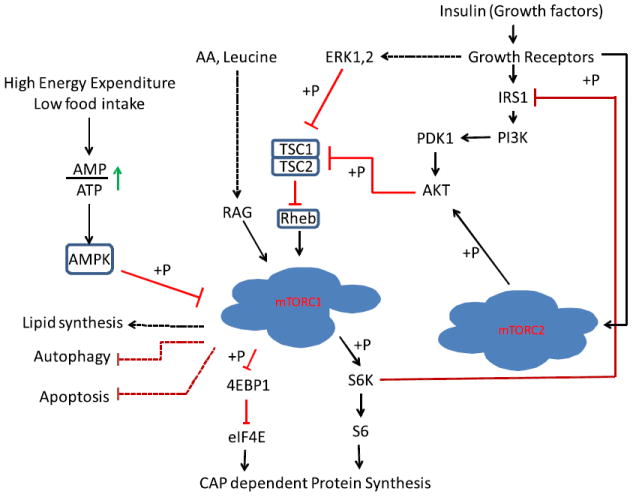
Regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTORC) signaling networks. Growth factors/mitogens (insulin, epidermal growth factor) and nutrients (eg, amino acids, energy) promote mTORC1 signaling via phosphorylation cascades that converge on tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and the mTORCs themselves. Insulin signals via its receptor (Insulin-R) to activate the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/TSC/Rheb pathway; amino acid sufficiency signals via hVps34 and the Rag and RalA guanosine triphosphatases; and energy sufficiency suppresses AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Insulin/PI3K signaling likely promotes mTORC2 signaling via an unknown pathway. An mTORC1/S6 protein kinase (S6K)-mediated negative feedback loop signals via 2 pathways to suppress PI3K/mTORC2/Akt signaling. AA, amino acids; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; 4EBP-1, 4E-binding protein-1; eIF4E, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E; ERK, extracellular signal–regulated kinase; IRS1, Insulin Receptor Substrate 1; PDK1, Phosphoinositide Dependent Protein Kinase 1; S6, S6 Ribosomal Protein.
