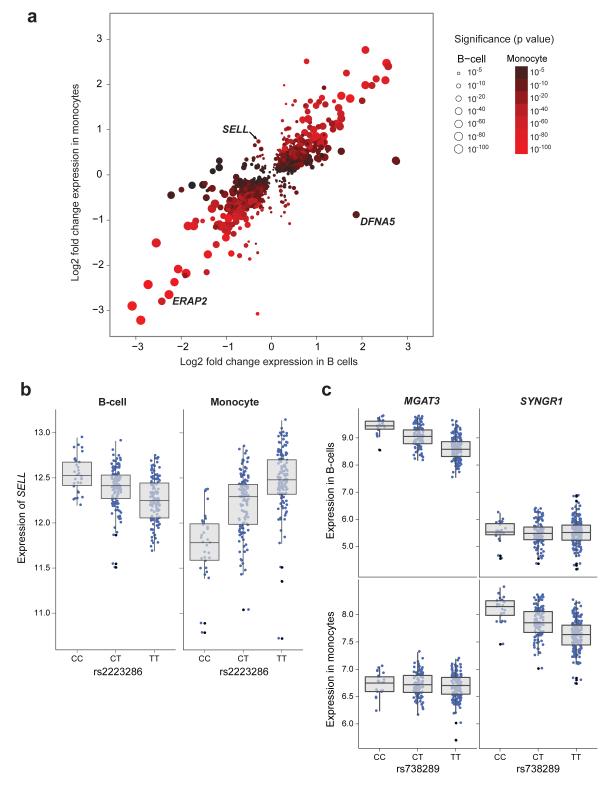
Figure 2. eSNPs shared between cell-types may lead to opposing directional effects on gene expression or associate with expression of different genes in a cell-specific manner.
(a) Using eSNPs shared between cell types the most significant eSNP per probe is plotted with the fold change in expression this eSNP causes in homozygous form between major and minor alleles (fold-change monocytes y- axis, B-cells x-axis). Whilst the majority of eSNPs shared between datasets cause the same directional change, there are examples of eSNPs that cause opposing directional changes in expression dependent upon cell-type. Only one eSNP is plotted per probe and only eSNPs with examples of >2 individuals homozygous in the minor allele with permuted p<0.001 in both B-cells and monocyte datasets are annotated. (b) rs2223286 is associated with profound directional effects in the expression of SELL dependent upon genotype, with the minor C allele associated with increased expression of SELL in B-cells and reduced expression of SELL in monocytes (pB-cell=4.6×10−11, pmonocyte=1.1×10−22). (c) rs738289 is an example of an eSNP that forms eQTL to differing genes dependent upon cell type. In B-cells this eSNP is strongly associated with the expression of MGAT3 (pB-cell= 9.8×10−26) with no association to SYNGR1 expression; whilst in monocytes this eSNP is significantly associated with the expression of SYNGR1 (pmonocyte = 1.2×10−17) with no association to MGAT3 expression.