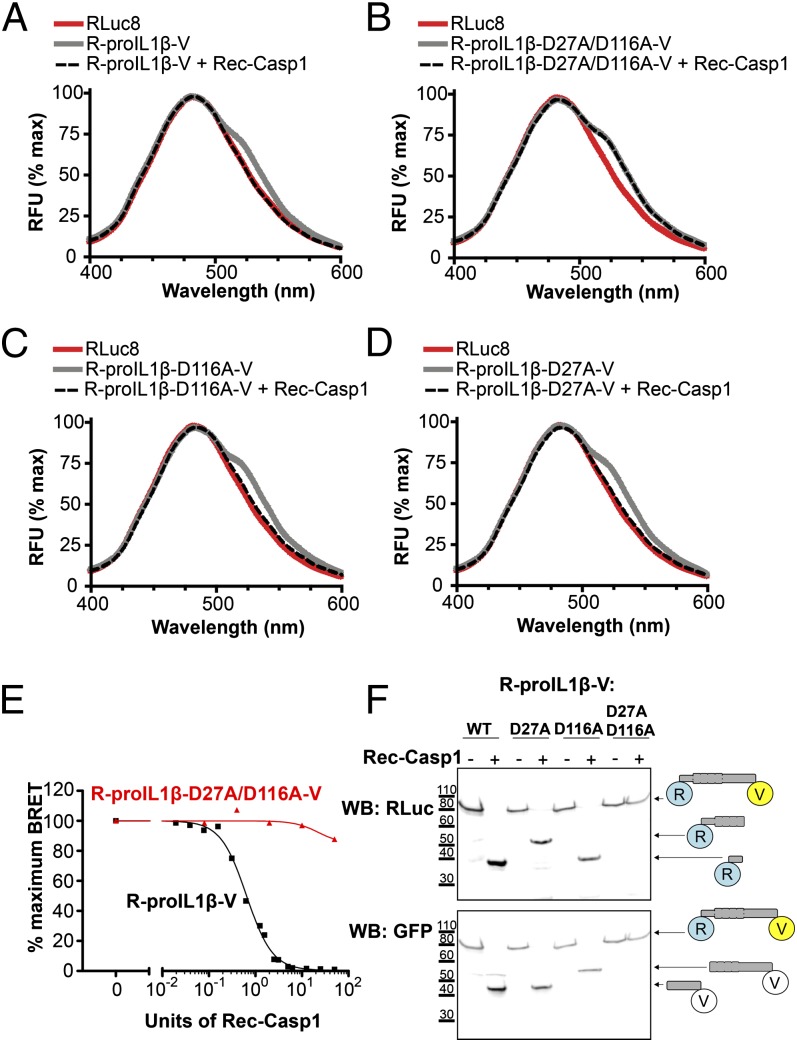
FIGURE 2.
Response of a BRET sensor to detect IL-1β processing in vitro. (A) Emission spectra of the R-proIL1β-V sensor. HEK293 cells expressing R-proIL1β-V or RLuc8 were solubilized and incubated for 1 h at 37°C with or without 50 U recombinant caspase-1 (Rec-Casp1). After adding coelenterazine h, emission spectra were measured. Note that the shoulder observed at 535 nm for the BRET sensor completely disappeared after addition of caspase-1. (B) Emission spectra of the R-proIL1β-V sensor mutated on the two caspase-1 cleavage sites on residues D27 and D166. Experiments were performed, as described in (A), on HEK293 cells expressing mutated R-proIL1β-V (R-proIL1β-D27A/D116A-V). Note that emission spectra of the double mutant superposed before and after incubation with caspase-1. (C and D) Emission spectra of the R-proIL1β-V sensor mutated on one of the two caspase-1 cleavage sites. Experiments were performed as described in (A). Note that shoulder observed at 535 nm for the BRET sensor completely disappeared after cleavage by recombinant caspase-1 for the two single mutants. Emission spectra from (A–D) are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Percentage of BRET signal measured for R-proIL1β-V and R-proIL1β-D27A/D116A-V constructs after incubation with different units of recombinant caspase-1. Dose-response curve is representative of three independent experiments. (F) WB analysis of R-proIL1β-V cleavage by Rec-Casp1. HEK293 cells expressing R-proIL1β-V, R-proIL1β-D27A-V, R-proIL1β-D116A-V, or R-proIL1β-D27A/D116A-V were treated as described in (A). R-proIL1β-V byproducts were analyzed by WB and compared with their expected size, as schematized on the right of the blot. The blot shown is representative of four independent experiments.