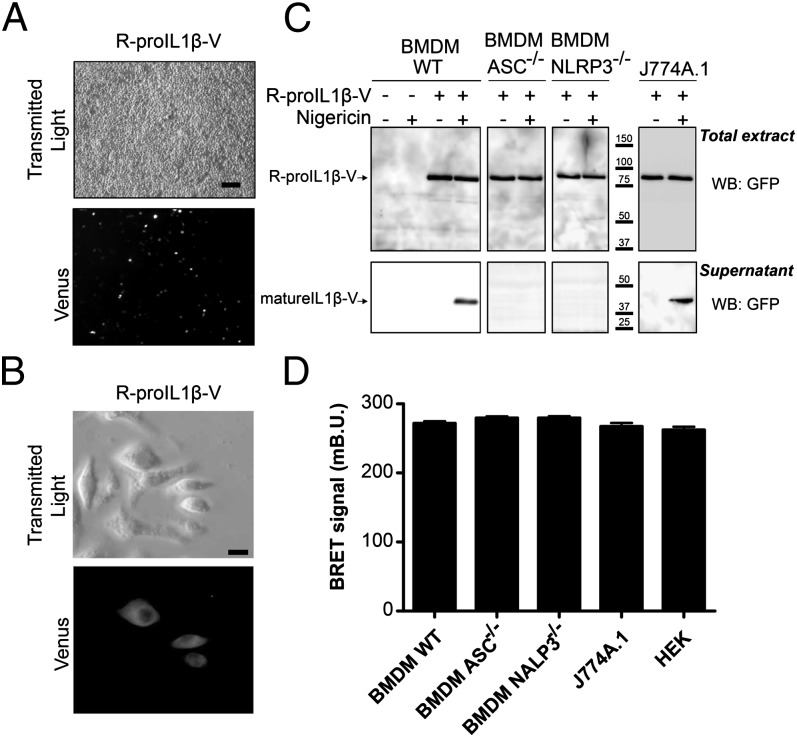
FIGURE 4.
R-proIL1β-V sensor has similar functional properties as endogenous IL-1β processing when transfected in macrophages. (A) Representative images of transfection efficiency of immortalized BMDM transfected with R-proIL1β-V. Twenty-four hours after transfection, R-proIL1β-V sensor was observed by microscopy after Venus excitation. Scale bar, 60 μM. (B) Representative image of R-proIL1β-V expression and its subcellular localization in J774A.1 macrophages. Experiments were realized as described in (A). Scale bar, 10 μM. (C) Macrophage activation induces R-proIL1β-V cleavage. Twenty-four hours after transfection with the R-proIL1β-V BRET sensor, immortalized WT BMDM or J774A.1 macrophages were primed with LPS (1 μg/ml for 4 h) and subsequently treated (or for controls not treated) with 5 μM nigericin for 30 min. Supernatant and lysates were analyzed by WB. In BMDM immortalized from ASC- or NLRP3-deficient mice, R-proIL1β-V was not cleaved after stimulation. The blot shown is representative of three independent experiments. (D) R-proIL1β-V displays similar BRET in resting macrophages. BRET signals were measured after R-proIL1β-V overexpression in HEK293, J774A.1, and immortalized BMDM from WT or ASC or NLRP3 knockout mice. Results are mean ± SEM of n ≥ 3 experiments and n ≥ 33 wells.