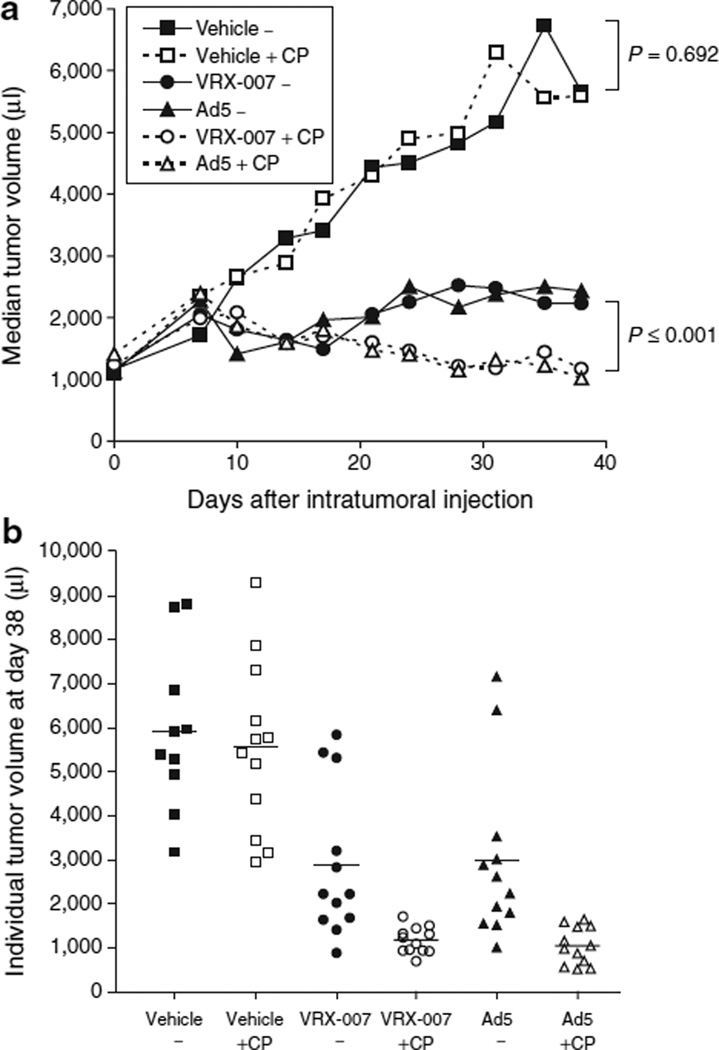
Figure 2. Immunosuppression with cyclophosphamide (CP) resulted in significantly enhanced tumor control with oncolytic adenoviruses (Ads).
Following randomization based on tumor volume, animals in treatment groups receiving CP were administered the first dose of CP on day −4. CP was administered twice weekly for the duration of the study. The immunosuppression data are shown in Figure 1. Animals received intratumoral injections of VRX-007, Ad5, or vehicle on days 0, 1, 2, 4–6 (n = 12 for each of six groups). The mean tumor volume on day 0 was 1,294 µl. Tumor growth was monitored by tumor measurement with digital calipers. Due to anemia in animals treated with CP, the study was terminated at 41 and 42 days. (a) Median tumor volumes (in microliters) are shown for each group for the duration of the study. Statistically significant differences were found between virus treatment alone (“VRX-007−” or “Ad5−”) and virus plus CP (“VRX-007 + CP” or “Ad5 + CP”), in which all P ≤ 0.001. No significant difference was detected between “Vehicle−” and “Vehicle + CP” (P = 0.692). All groups that received intratumoral virus treatment showed statistically significant tumor suppression when compared with “Vehicle−” or “Vehicle + CP” (P ≤ 0.004 for all such comparisons). (b) Individual tumor volumes (in microliters) at the last tumor measurement, on day 38, are shown. Each point represents one animal and the bar represents the mean volume for each treatment group.