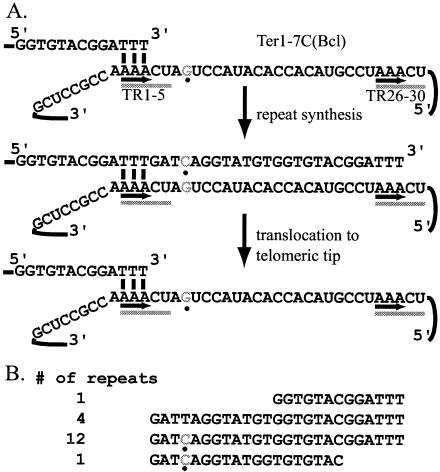
FIG. 1.
Wild-type telomerase translocation. (A) A diagram of telomerase translocation in K. lactis is shown; the labeling in this diagram will be continued in all subsequent diagrams. The allele TER1-7C(Bcl) is shown, with the point mutation shown in gray and marked with a black dot. The mutation name refers to the point mutation incorporated into the telomeric strand. A short region of the telomeric repeat is shown base pairing with TR1-5 of the template. TR1-5 and TR26-30 are shown underlined with a gray bar. The region between the underlined segments is the 20-nt core of the template. The nucleotides involved in base pairing are underlined with a black arrow; in this model, telomerase synthesis is shown to stop at position 28, so there are 3 nt available to align with the template. Alignment begins at position 1 of the template. Once synthesis is complete, telomerase can dissociate and realign for the next round of telomeric repeat synthesis. (B) The sequence of a telomere cloned from a strain containing TER1-7C(Bcl) is shown. This telomere contains 16 complete telomeric repeats, in addition to the partial repeats at each end. The sequence is shown from the subtelomere-adjacent sequence (top) to the tip of the telomere (bottom). The point mutation is copied into each newly synthesized telomeric repeat. In all figures, the first full line of sequence is the complete 25-bp repeat; all variations can be compared to this line. The point mutations are shown in gray type and marked with a black dot. The number of each type of repeat is shown at the right. The repeat at the tip varies from the penultimate repeat only because it is not a complete repeat.