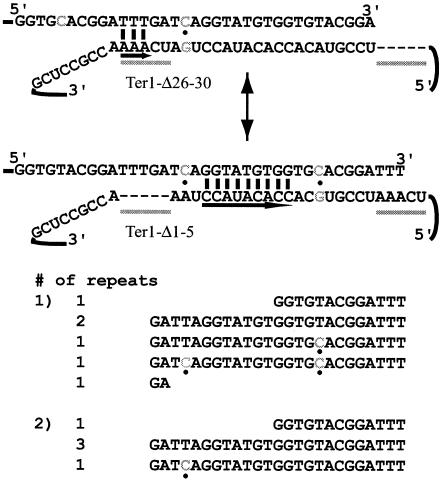
FIG. 2.
Two telomerase molecules can work cooperatively to synthesize a telomeric repeat. A model for telomerase translocation in cells containing ter1-Δ26-30 and ter1-Δ26-30 is shown. The positions of the deleted nucleotides are marked with dashes, and the regions of the TRs are underlined with gray bars. The telomerase shown at the top, from the ter1-Δ26-30 mutant, also contains a 7C point mutation (shown in gray and marked with a dot). This molecule can base pair by using TR1-5 but lacks TR26-30. The second molecule, from the ter1-Δ1-5 mutant, could base pair by using nucleotides in the template core (underlined with a long black arrow) and is marked with the 20C (shown in gray and marked with a dot) mutation. Note that, in order for the 20C mutation to be incorporated, loss of some telomeric sequence is necessary after synthesis by the ter1-Δ26-30 telomerase. Telomeres cloned from the heteroallelic strain are shown below the model. In one telomere, incorporation of both point mutations can be seen (gray nucleotides, marked with dots); in the other, only one has been incorporated.