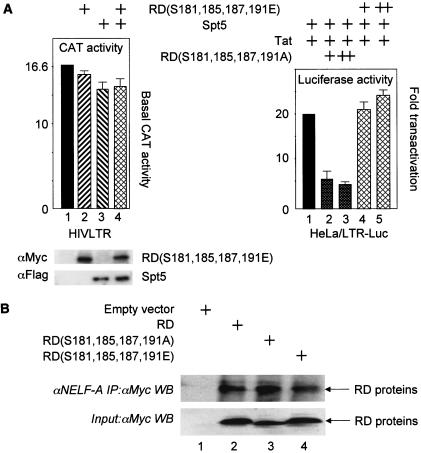
FIG. 5.
Effects of mutant RD proteins on viral transcription and their incorporation into NELF. (A) (Left) The mutant glutamate-substituted RD protein no longer inhibits HIV transcription. pHIVCAT, mutant RD(S181,185,187,191E) and Spt5 were expressed in HeLa cells, and CAT assays were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1A. (Right) The mutant alanine-substituted RD protein inhibits Tat transactivation. Tat (0.1 μg), Spt5 (0.1 μg), mutant RD(S181,185,187,191E) (0.1 and 0.3 μg) or mutant RD(S181,185,187,191A) (0.1 and 0.3 μg) proteins were expressed in HeLa cells that stably contained the HIVLTR linked to the luciferase reporter gene. Luciferase activities were measured 48 h later. (B) Wild-type and mutant RD proteins are incorporated equivalently into NELF. 293T cells expressed Myc epitope-tagged RD proteins. Immunoprecipitations (IP) with the anti-NELF-A monoclonal antibody (αNELF-A)were followed by Western blotting (WB) with the anti-Myc antiserum (αMyc). The bottom gel contains 5% of input proteins. In lane 1, cells were transfected with the empty plasmid vector. Arrows point to wild-type and mutant RD proteins in lanes 2, 3, and 4.