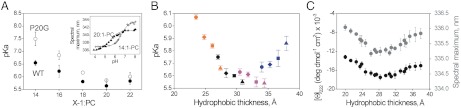
Fig. 3.
Insertion pKa is affected by both acyl chain length and cholesterol. (A) Membrane insertion pKa for WT (closed symbols) and P20G (open symbols) in liposomes of different acyl chain length. pKa values were determined from fluorescence spectra maxima at different pH values, as the midpoint of the sigmoidal transition (36), as shown in the inset for 20∶1-PC and 14∶1-PC. (B) Correlation between pHLIP insertion pKa and membrane hydrophobic thickness. Liposomes of PC lipids of different chain length (16∶1-PC, orange; 18∶1-PC, black; 20∶1-PC, magenta; 22∶1-PC, blue); containing 0% (circle), 10% (diamond), 20% (square), and 30% (triangle) cholesterol. Hydrophobic thickness refers to the distance between the acyl chain carbon 2 of the two hemilayers, as determined by small-angle X-ray scattering (30). The thickness increase associated with cholesterol was extrapolated from (49). Data points for 14∶1-PC lipids were not included, as explained in Fig. S9. (C) CD and fluorescence values for pHLIP state III. The ellipticity at 222 nm (left axis) and fluorescence spectral maximum (right axis, grey symbols) are plotted for the hydrophobic thickness of the different PC lipids at 0, 10, 20 and 30% cholesterol. Experiments were performed at 28 mM acetic/acetate buffer, pH 4.5.