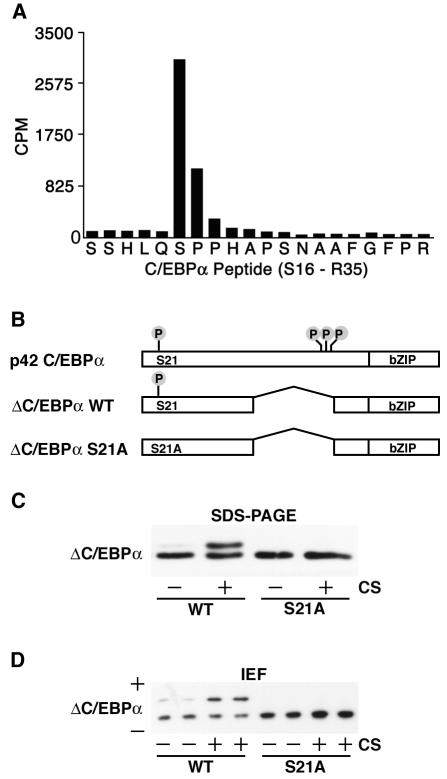
FIG. 1.
Phosphorylation of C/EBPα on serine 21. (A) In vivo labeling of C/EBPα was performed to identify phosphorylated residues. 32P-labeled C/EBPα was purified, cleaved with trypsin, and separated by high-performance liquid chromatography. Fraction 87 was found to contain radioactivity, and sequencing revealed it to be amino acids S16 to R35 of C/EBPα (x axis). The radioactivity associated with each amino acid was quantified (y axis; counts per minute [CPM]). The majority of the radioactivity was found in the sixth cycle, corresponding to serine 21. (B) Schematic representation of C/EBPα proteins engineered for further experiments. Four known phosphoamino acids, S21 (identified herein), T222, T226, and S230 (previously identified [37]) are illustrated. WT, wild type. (C) 3T3-L1 cells were infected with retroviruses carrying the genes for ΔC/EBPα and ΔC/EBPα-S21A. Cells were not treated (−) or treated (+) with 10% calf serum (CS) for 10 min prior to lysis and purification of nuclear proteins. Nuclear lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed for C/EBPα by immunoblotting. (D) Samples from panel C were separated by isoelectric focusing (IEF) and analyzed for C/EBPα by immunoblotting. Acidic (+) and basic (−) ends are indicated. Similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments.