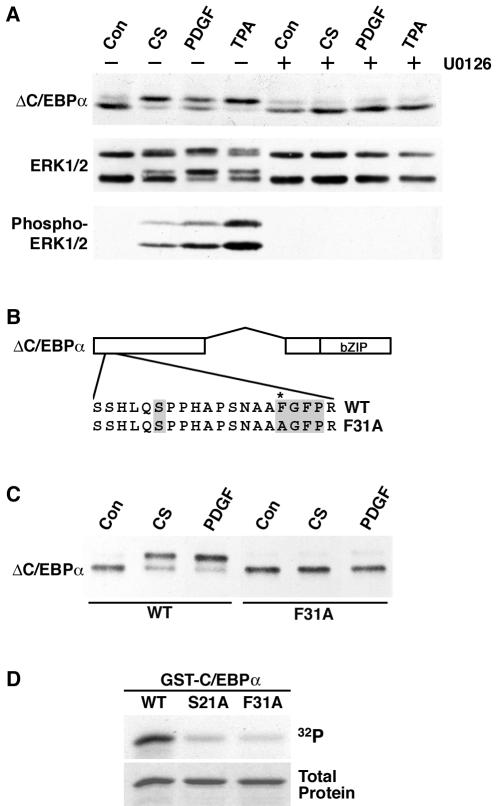
FIG. 2.
ERK1/2 phosphorylates C/EBPα on serine 21. (A) 3T3-L1 cells were infected with a retrovirus carrying the gene for ΔC/EBPα. ΔC/EBPα-expressing cells were pretreated for 15 min in the absence (−) or presence (+) of the MEK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) prior to treatment with vehicle (Con), 10% calf serum (CS), 25 ng of PDGF per ml, or 100 nM TPA for an additional 10 min. Lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis for C/EBPα, ERK1/2, or phospho-ERK1/2. ERK1, which migrates with an apparent mobility of 44 kDa, is the upper doublet, and ERK2, which migrates with an apparent mobility of 42 kDa, is the lower. (B) Schematic representation of C/EBPα and a C/EBPα docking site mutant engineered for use in further experiments. The ERK docking site and serine 21 are shaded. The asterisk (*) indicates the phenylalanine that is converted to alanine in the docking site mutant form. WT, wild type. (C) 3T3-L1 cells were infected with retroviruses carrying the genes for wild-type and F31A mutant ΔC/EBPα. Cells were not treated (Con) or treated with 10% calf serum (CS) or 25 ng of PDGF per ml for 10 min. (D) In vitro kinase assays were performed with recombinant ERK2 and GST fusion proteins containing the first 139 amino acids of C/EBPα (WT) or the same region with the indicated point mutations (S21A and F31A). Proteins separated by SDS-PAGE were stained with Coomassie blue (bottom) and subjected to autoradiography (top).