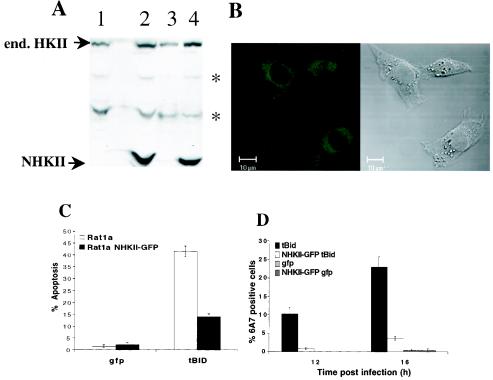
FIG. 7.
Overexpression of mitochondrially bound HKII inhibits tBID-mediated apoptosis and BAX activation. (A) Whole-cell extracts (lanes 1 and 2) and mitochondrially enriched fractions (lanes 3 and 4) of a polyclonal Rat1a fibroblast cell line stably overexpressing the N-terminal, mitochondrially bound catalytic half of HKII (lanes 2 and 4) and parental Rat1a fibroblasts (lanes 1 and 3) were analyzed for expression of endogenous (end.) HKII and exogenous NHKII by immunoblotting with anti-HKII antibodies. Asterisks, nonspecific bands. (B) Confocal image of GFP fluorescence and the corresponding Nomarski image of Rat1a cells stably overexpressing NHKII-GFP. (C) Polyclonal Rat1a fibroblasts stably overexpressing the N-terminal, mitochondrially bound catalytic half of HKII and parental Rat1a fibroblasts were infected with tBID-expressing retrovirus, and apoptosis was quantitated by DAPI staining 16 h postinfection. (D) Experiment performed as for panel A, except that cells were fixed 12 and 16 h postinfection and immunofluorescence staining for activated BAX was performed. All data are depicted graphically as the means ± standard errors of the means for three independent experiments.