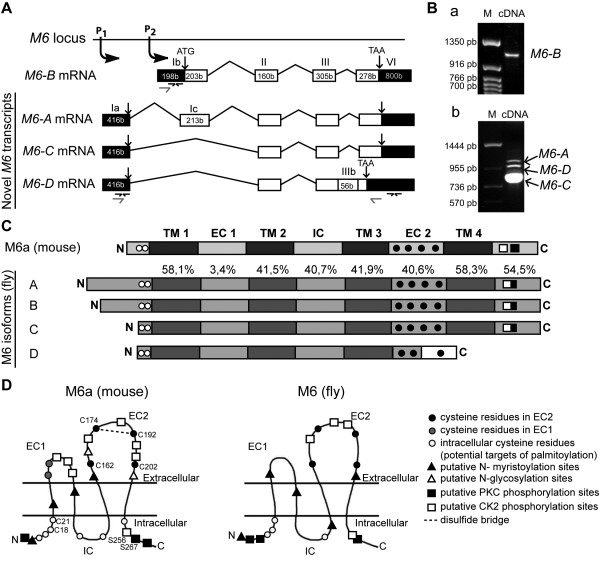
Figure 1 .
M6 isoforms are structurally conserved inDrosophila. (A) Schematic diagram (not scaled) of the M6 locus shows the novel M6-AM6-C and M6-D transcripts from promoter 1 (P1) and M6-B from P2. Exons (boxes), introns (lines), untranslated regions (UTR, dark boxes) and coding regions (white boxes) are represented. Numbers in each box indicate nucleotide length (in bases). Roman numbers denote exons according to Schweitzer J. et al [5]. The sequences for M6-A/C/D are [GenBank: JN872491, JN872492, and JN872493], respectively. The previously reported sequences M6-1 [GenBank: AAF71284] and M6-2 [GenBank: AAF71285] correspond to M6-C and M6-B isoforms, respectively. Primers to quantify M6 levels by RTqPCR are indicated by black arrows. (B) Detection of M6 expression by RT-PCR. cDNAs from w heads were amplified using primers (gray arrows) annealing on (a) the exon Ib (5’UTR of M6-B) and the exon VI (coding region) and on (b) the exon Ia (5’UTR of M6-A/C/D) and the exon VI (coding region). M, nucleotide marker. (C) Schematic representations of M6a and M6 protein topology (not scaled) predicted from the PredictProtein server. Transmembrane domains (TM, dark gray boxes), extracellular and intracellular loops (EC and IC, gray boxes) are flanked by cytoplasmic N and C. Amino acid similarities among each M6-isoform domain are relative to M6a (in percentage). M6-A/B/C are identical between them in each domain except for the N. The frame shift sequence (white box) of M6-D isoform is indicated. Conserved Cys residues C18/21 and C162/174/192/202 in N and EC2 (black and white circles) are according to mouse M6a sequence. (D) Putative post-translational modification sites conserved between M6a and M6. These sites were predicted using the PROSITE motif search. The M6 representation corresponds to M6-A/B isoforms. M6-C/D do not have either the putative phosphorylation sites or the N-myristoylation site. M6-D isoform also lacks the CK2 phosphorylation, the N-myristoylation sites from the EC2 domain and the PKC and CK2 phosphorylation sites corresponding to the C. CK2 and PKC phosphorylation sites (white and black squares, respectively) are conserved at the C. N, N-terminus; C, C- terminus.