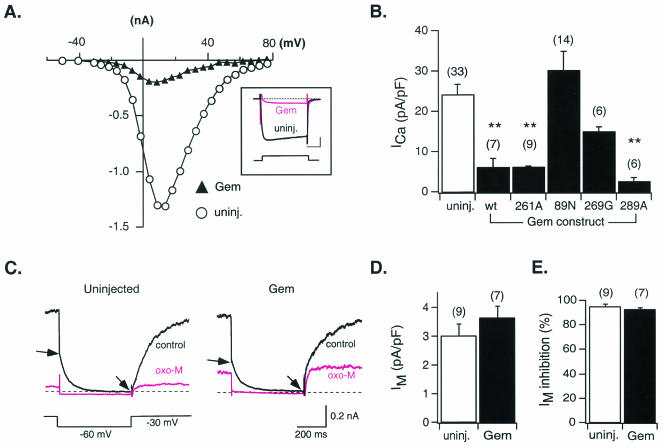
FIG. 4.
Effects of heterologous Gem expression on N-type Ca2+ and M-type K+ channels of sympathetic neurons. (A) Current-voltage relationships for Ca2+ currents (ICa) recorded from a control neuron (uninjected; open circles) and one injected approximately 24 h earlier with Gem cDNA (filled triangles). The inset illustrates superimposed ICa traces evoked by a 70-ms voltage step to +13 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Calibration bars, 20 ms (horizontal) and 0.3 nA (vertical). (B) Average ICa density (± SEM) in uninjected neurons (open bar) and neurons injected with wild-type (wt) or mutant Gem cDNA (filled bars) as indicated. ICa density was calculated from the ICa amplitude at a test pulse of +10 mV normalized to cell membrane capacitance. (C) Representative current traces of the K+ current arising from M-type channels (IM) recorded from a control neuron (left) and a neuron previously injected with Gem cDNA (right) in the absence (control) or presence of 10 μM OXO-M. IM amplitude was measured as the difference in current magnitude between the beginning and end of a 500-ms hyperpolarizing voltage step to −60 mV (arrows). (D) Average IM density (± SEM) measured from control neurons (open bar) and neurons previously injected with Gem cDNA (filled bar). IM density was determined by normalizing IM amplitude (see above) to membrane capacitance. (E) Average percent inhibition (± SEM) of IM produced following OXO-M (10 μM) application in control neurons (open bar) and neurons previously injected with Gem cDNA (filled bar). Number of neurons tested is shown in parentheses. **, P < 0.01.