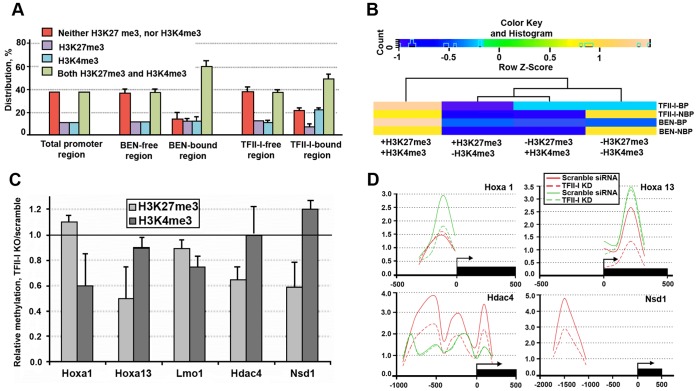
Figure 6. TFII-I binding overlaps with bivalent domain in ESCs. (.
A) The promoter occupancy by TFII-I and BEN correlates with genome-wide distribution of H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 bivalent marks (green bars). (B) Heat map indicates the co-localization frequency of TFII-I and BEN with bivalent domain. TF2I-BP, TFII-I bound promoters; TF2I-NBP, promoters free of TFII-I; BEN-BP, BEN bound promoters; BEN-NBP, promoters free of BEN. (C) Depletion of TFII-I by siRNA knockdown reduces H3K4me3 at Hoxa1 and H3K27me3 at Hoxa13, Hdac4 and Nsd1. (D) ChIP revealed that TFII-I depletion affects H3K27me3 at the promoters of Hoxa13, Hdac3 and Nsd1 and H3K4me3 at the Hoxa1 promoter. H3K27m3 is in red; H3K4me3 is in green.